
SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
UNIT – I - OFFICE MANAGEMENT – SBAA1407
1
I. FILING AND INDEXING
1.1 DEFINITION OF OFFICE
―An office is the administrative centre of a business. The purpose of an office has been defined
as the providing of a service of communication and record‖- Mills & Standing Ford.
―An office is a place where business is transacted or professional service is available‖-
1.2 FUNCTIONS OF MODERN OFFICE
I
Basic Functions
Receiving and collecting information
Recording information
Arranging and processing of information
Storing of data
Communication of recorded data
II
Administrative functions
Management functions
Office systems and procedures
Designing and purchasing of office forms and stationery
Selection and purchase of office furniture, equipments and machinery
Public relation function
Retention of records
Safeguarding of office assets
Controlling office cost
I.
Basic Functions (or) Routing Functions:
(a)
Receiving and collecting information: It is the primary function of office to receive and
collect the information for timely business decisions. Information is generally collected both
from Internal sources such as letters, memos, circulars, notices etc., issued by different
departments, sections and External sources like government departments, financial
Institutions, banks, suppliers, customers, universities, general public etc.
(b)
Recording of information: The collected Information has to be recorded for future
reference in a suitable form. This recorded information is needed for preparing future plans,
policies and taking decisions.
(c)
Arranging (or) Processing of Information: All the information received cannot be used
as it is. Office has to convert the collected information in the form of notes, reports,
2
diagrams, graphs etc., depending upon the nature of information for easy access and
understanding.
(d)
Storing Data: The recorded information should be protected for future reference. The
degree of necessity of data will determine the duration for protecting the same. Based on the
importance of data, office will store them in a separate file.
(e)
Communication of Recorded Data: Office has to supply the right information at the
right time to different departments and also to outside bodies who are related in some way or
the other for prompt and sound business decisions.
II.
Administrative Management Functions:
For the smooth functioning of the office there are certain administrative functions needed to be
performed. These functions are outlined below:
1.
Management Functions: Office work has to be properly planned, organized and executed
according to the plan. For efficient functioning of an office the manager has to perform the
following function such as.
Planning.
Organizing.
Staffing.
Directing.
Communication.
Controlling.
Co-ordination.
Motivation.
2.
Developing Office Systems and Procedures: Most important function of the office is to plan
and set up suitable systems and procedures for the major activity of office. For the efficient and
economical performance of office operations, each major work of the office is to be carefully
planned and also the routine procedures for performing them to be determined beforehand
itself.
3.
Form Designing and Control: A form is a standardize record, which is used to accumulate
and transact information for reference purposes. These forms serve as a storehouse of
information. Since the office work is largely paper work, the form used should be designed so
as furnish the required information in an appropriate manner. It is the duty of the office to
design the forms that can be used in various departments.
3
4.
Purchasing and Supply of Office Stationery: Majority of office work are paper work.
Consequently adequate supply of office stationery of suitable quality is of prime importance
for the systematic and efficient performance of office work. It is the task of office to look after
the standardization, selection, and purchase of office stationery and its distribution to different
departments.
5.
Selection and Purchase of Office Furniture, Equipment and Machines: The office has to
select and purchase the right type of furniture, equipment and machines in right quantities, so
that office work can be carried out according to the planned system and routine without any
interruptions and must also ensure their fullest utilization in the organization.
6.
Public Relations Functions: An office has not only maintained relations with the other
departments, it also needs to maintain a good dealings with the outside world such as
suppliers, customers, bankers, government departments and the public at large. Maintaining
good relations with these stakeholders increases the reputation and goodwill of the company.
7.
Retention of the Records: Records are those documents which serves as objective evidence
of activities performed, events occurred, results achieved, or statements made. They are created
/received by an organization in routine transaction of its business or in pursuance of its legal
obligations. Office retains records such as correspondence, invoices, orders, financial and cost
records, and minutes etc., for future reference.
8.
Safeguarding Assets: It is one of the functions of office to safeguard the assets of the
organization, such as immovable assets like buildings, plants, machinery, office equipment,
lighting and air conditioning equipment, and movable assets like furniture, office machinery,
title deeds, records and documents, or cash, etc., against loss or damages from unforeseen
conditions.
9.
Controlling office Costs: With the adoption of scientific methods in office management, a
modern office discharges the function of controlling office costs through (a) Mechanization of
the office. (b) Adopting time and labour saving devices in the office. (c) Using better forms. (d)
Analyzing the existing office routines and adopting improved ones.
1.3 IMPORTANCE OF OFFICES
An office is an important unit of the whole organization which is also regarded as the
mainspring of a watch. It has its equal importance in the government sector as well as in the
private sector. It is essential for the office to perform a number of administrative as well as
clerical functions in the process of achieving the organizational objectives.
4
(a)
Information Center: The office serves as an information center. It collects information
from sources like invoices, letters, memos, agreements, vouchers etc., and protects them in safe
mode on the basis of their importance for future reference.
(b)
Proof of Existence: The office is the evidence for existence and survival of business. As
office coordinates the functions of different departments of an organization, without office no
business house can survive. People tent to generalize about the existence of business only with
the help of regular functioning of an office.
(c)
Channel of Communication: The office is the channel of communication between
different people and department of business. The staffs working at various levels of managerial
hierarchy are linked with one another through office. Office transmits the information about the
functioning of different departments such as personnel, finance, production and marketing with
each other.
(d)
Co-Ordination of Work: Business is divided into department and subunits for bringing
simplicity in the operation. The office will work as a coordinator to maintain the relationship
between departments. It develops productivity relationship to achieve common goals of an
organization.
(e)
Centre for Formulation and communication of plan and policies: A business is
established with the objective of attaining the certain result. To achieve this result top level
manager formulate plans and policies from office. These plan and policies are communicated
to related person through the office. Therefore, the office is a center for the formulation and
communication of plans and policies.
(f)
Managerial Control: The process of developing performance standard and comparing with
actual performance in order to take corrective action for deviations if any is called controlling.
The office helps in controlling the activities of different people and department of an
organization. Through controlling it ensures that the various activities of business are
performed with much accuracy.
(g)
Memory Center: Office protects important information of past in a safe manner. The
departments and people generally collect needed data from the office as and when they are
required. It provides information storage facilities in the form of files and devices on the basis
of their importance for future reference. Therefore, the office is considered as memory center.
(h)
Service Center: The office works as a service center for different units and departments of
an organization. It provides clerical services like mailing, filing, typing, printing, supplying
resource etc., to all people working in different departments of an organization.
5
1.4 TYPES OF OFFICE:
Front office: The front office otherwise called reception. It refers to a company‘s
department that come in contact with outsiders such as clients, suppliers, bankers, financial
institutions and general public at large. The front office welcomes visitors, deals with queries
of the visitors, and receives mails and disseminates the same to respective departments.
The Middle Office: The middle office is usually a part of operations division of the
business unit. These divisions ensure the proper flow of work within the organisation. Middle
office generally functions along with the front office and it comprises of departments of
financial services. Due to their critical role, it is supervised by the back office managers.
Electronic Office: It is integrated computer systems designed to handle office work. In
this office all the activities are carried out with the help of software applications. The aim of e-
office is to reduce paper work and speed up business operations. The introduction of e-office
improves accuracy and efficiency of organizations and thereby improved their level of service
Virtual Office: ―Virtual Office‖ implies mobile or remote work environment equipped
with telecommunication links and basic office furniture, but without a fixed office space.
Office automation has led to the development of virtual office concept. It works just like a
physical office but without physical space and facilities. Employees interact with others
through portable communication tools such as electronic mail, cellular phone, voice mail
system, laptop computer, fax machine, and audio/video conferencing system. Employees
armed with these tools can perform their work from any place — their homes, cars, restaurants,
airports, customers‘ offices, and so on.
Back Office: These offices are generally found in operating corporate organizations
where tasks dedicated to operating the company are performed. The term comes from the
building layout of early organizations here the front office would contain the sales and other
costumer-facing staff and the back office would be those manufacturing or developing the
products or involved in administration but without being seen by customers. Although the
operations of back office are usually not given a lot of consideration, their contribution to the
business is significant.
1.5 OFFICE MANAGER
An office manager is an individual, who is in-charge of an office and whose function is to
organize and control the activities of the office. He is appointed to head the office. ―The office
manager is the pivot around which the office function revolves‖ (Denyer, J.C.).He extracts the
work from the subordinates to achieve organizational goals. It is his responsibility to plan,
organize and control the clerical aspects of the organization including the preparation,
6
communication, coordination and storage of data to support production and other important
operations of industrial establishments. He monitors the work processes and evaluates their
outcome. On the whole he is appointed as an administrative head of office. Today, in the
modern era of dynamic and competitive business environment, the office manager has to
perform a wide variety of tasks from managing basic office services to handling of the most
modern techniques of systems integration, automation, operations research and communication.
In performing these tasks he assumes the position of a full-fledged functional executive at par
with other operational executives.
1.5.1 QUALIFICATIONS OF OFFICE MANAGER:
(i) Education and Practical training,
(ii) Experience and
(iii) Personal qualities.
(i) Education and Practical training: An office manager must have appropriate
educational qualifications. He should possess not only bachelor‘s degree in the relevant
discipline, but also have proficiency in English and one or more foreign languages. The office
manager must also have special training in business administration, accounting, office systems
and procedures, office machines and data processing methods.
(ii) Experience: He should have sufficient business experience preferably be in a similar
organization as the one employing him as office manager. This will enable the office manager
to get familiar with the routine procedures of the organization and also the problems of the
office that he has to manage.
(iii) Personal Qualities: The main task of the office manager is to get the office work done
by personnel of the office efficiently and economically. To achieve this objective he must be
able to organize, inspire and lead the staff under him. He must also try to understand the ability
and aptitude of each individual worker and delegate work to them accordingly. For this he must
possess a number of personal qualities such as leadership, sound judgment, sense of justice and
fair play, impartiality, sincerity, understanding of human nature, tact, persuasiveness etc.
1.5.2 FUNCTIONS OF OFFICE MANAGER
1.
Managerial Functions
2.
Supervisory Functions
3.
Personnel Functions
4.
Duties to the Management.
7
1. Managerial Functions: The office manager is the administrative head of office. It is his duty
to manage the entire affairs of an office. As an administrative incharge, he is expected to
perform the following functions.
Planning the work to be performed before hand.
Forecasting the future demands based on past records.
Organising the activities of office.
Co-ordinating the activities of various departments.
Executing the policies and programmes of the management.
Communicating various policy decisions to the functional managers.
Designing and implementing new systems and procedures.
Reviewing system and procedures periodically and effecting changes in them.
2. Supervisory Functions: The prime duty of office manager is to extract the work from
subordinates. In this regard, he performs the following supervisory functions:
Dividing and allocating the work among the subordinates based on their
specialisations.
Ensuring that the work is carried out as per predetermined schedule.
Exercising regular control over the quantity and quality of the work done by the
subordinates. d. Ensuring the punctuality.
Providing adequate stationery and supplies and controlling their usage.
Arranging for appropriate equipment and maintaining them in proper working
conditions.
Maintain the office, well organised, clean and tidy.
3. Personnel Functions: At times office manager acts as a human relation officer for his own
department. To ensure higher degree of accuracy and efficiency at work he should have efficient
subordinates. For that purpose he discharges the following duties.
Recruit or hire skilled workers for the departments.
Arranging for training and development programmes for the subordinates to upgrade
their knowledge.
Conducting staff appraisal interviews periodically.
Measuring the work of subordinates through appropriate methods.
Fixing up remuneration for the staffs and devising methods for suitable compensation.
Dealing with matters as regards to indiscipline.
Counselling and settling the disputes among the subordinates to the possible extent.
8
4. Duties to the Management: manager is a functional head of the department. He acts as staff
expert to top management and offers advices on various policy matters relating to office routine.
He also performs the functions like
Provision of information that is needed to make policy decisions.
Supporting and implementing the policies of the top management.
Reporting the problems to the management which are beyond his limits.
Identifying problems in the implementation of the policies and reporting to the top
management for remedial action.
Handling mails and fixing up appointments on behalf of top managers.
1.5.3 QUALITIES OF GOOD OFFICE MANAGER:
In the recent years the authority and responsibilities of office manager have grown substantially.
They are more involved in policy decisions. The office manager should be capable to face
challenges of modern complexities of business world. Dynamic office manager possess the
following qualities.
1. Organising Ability: A modern office manager must be a good organiser. He should
organize the office services in such a way that it can be performed smoothly, efficiently and
economically. He has to act in the following manner:
2. Dynamic Leadership: He should be an energetic leader. He should inspire and build
confidence in the minds of the subordinates. He must also encourage the subordinates to
perform their job effectively and efficiently to achieve the common goals of an organisation.
3. Innovative: He should be innovative. He should have creative thinking and capability to
develop better methods and systems. Moreover, he should always in search of new and
innovative methods and techniques of doing the office work in order to increase the efficiency
and quality of the work.
4. Ability to Delegate: Office manager should be competent to divide and allocate the job
among the subordinates according to their capabilities. Effective delegation of authority ensures
accountability among subordinates and indirectly boosts their moral to a higher level.
5. Development of Personnel: He should be a demographic leader. He must encourage the
subordinates to carry on their routine work without his interventions and also allow them to
participate in the decisions relating to their work. He must conduct staff appraisal periodically to
identify their progress and accordingly arrange for training and development programmes for
their self-up gradation.
6. Forward Looking: The office manager should be forward looking. He should be competent
9
to forecast the future, visualize the future problems and devise plan to avoid such problems. E.g.
heavy competition, fall of demand, price hikes etc.,
7. Other Qualities: In addition to the above mentioned qualities, the office manager must have
highest level of integrity and should be honest and ethical in his dealings with everyone both
inside and outside the organisation. He should be freely contacted and consulted by people from
all the departments in the organisation. He should be able to handle situations diplomatically.
1.6 RECORDS MANAGEMENT
The very existence of business organizations, government and other social institutions is based on
records. Keeping good records is very important to any business. Record keeping system should be
accurate, reliable, easy to follow, consistent as to the basis used and be very simple. Good record
keeping is vital in regards to meeting the financial commitments of the business and providing
information on which decisions for the future of the business can be based.
While business maintains the records to monitor and to record normal business activities, it is also
necessary because of obligations under the taxation laws. These records are official documents and
also serve as legal evidence in case of emergencies.
In day to day business operation many documents are received, sent out and created. These
documents play a very important role in business operation and for taking some decisions. So such
documents should be preserved to obtain at the time of need. For that a filing system is developed
in every organization. Filing is the memory of any organization. Hence, filing is the process of
systematic and scientific preservation of official document for future reference or evidence. It is
putting the documents, letters etc into a file. It is a scientific and systematic process of saving
important documents for future reference.
Definition
It is that area of office administration which is concerned with creation, presentation, and use and
disposal of records. According to Jane K Cruible ―Records management refers to the activities
designed to control the lifecycle of a record from its creation to its ultimate disposition.
The functions of records management under these stages are discussed below.
1. Creation of Records: New forms and records should be developed carefully . Data should be
recorded in the documents accurately and completely.
2. Storage of Records: The storage is concerned with the classification of records and then filing in
the suitable filing equipment which is in the easily accessible location. Arrangement should also be
made to protect the records against disaster or unauthorized use.
10
3. Retrieval of record: The records are store for further use. An efficient procedure must be
established so that records may be retrieved and delivered in time.
4. Disposal of records: The last stage in the record cycle is the disposal stage which
is concerned with preserving valuable documents and disposing the expired documents. A record
retention schedule classifies records based on the time period and the requirement of the same.
1.6.1 OBJECTIVES OF RECORD MANAGEMENT:
1. To keep an Orderly Account of Progress: The purpose of writing down and
preserving memoranda of transactions, (financial and other kinds) various documents, papers,
correspondent etc, are to record the progress of the business.
2. To Facilitate Comparison: Records facilitate comparison between one period of time and
another, between different product lines and between firms operating in different lines of business.
3. To Detect Errors and Wastes: Records management is a control function which facilitates the
evolution of techniques for the elimination of errors and waste.
4. Legal Formalities: Certain records are to be kept for a specified period of time under the
provisions of the various Acts. For instance, receipts and payment vouchers and accounts books
have to be kept for several years under the Income Tax Act and so on.
1.7 FILING
Filing is the process of organising the correspondence and records in a proper sequence so
that they can be easily located. The term filing may be defined as the process of so arranging and
storing original records or copies of them, that they can be readily located when required. It
involves placing of documents and papers in acceptable containers according to some
predetermined arrangement so that any of them when required may be located quickly and
conveniently.
Definition
According to Zane K. Quible, ―Filing is one of the activities in the records management
programme which involves systematically classifying, coding, arranging and placing of records in
storage‖. G.R Terry has defined filing as ―the placing of documents and papers in acceptable
containers according to some predetermined arrangement so that any of these may be located
quickly and conveniently, when required‖.
1.7.1 Objectives
The major objectives of filing process are to ensure proper arrangement, careful storing and easy
availability of records. An efficient filing system is expected to have the following objectives:
i) To classify and arrange records properly.
11
ii) To protect documents against possible loss or damage.
iii) To provide a method of obtaining information without loss of time.
iv) To enable past records to be made easily available to management for framing business
policies and future plans.
1.7.2 Functions Of Filing System
Classification of documents on a pre-determined basis.
filing of letters and other documents after action taken in cardboard file covers or folders.
Preservation of file covers or folders in cabinets fitted with drawers.
Issue of files on requisition by any department.
Transfer of papers no longer in current use from the existing files to separate folder or
box files at regular intervals for possible future use.
Disposal of old papers and records when these are no longer useful.
1.7.3 Advantages Of Filing System
Records are stored under a suitable system of filing in order to achieve the following purposes and
benefits.
1. Ready Reference:
Records constitute the storehouse of information relating to past events. They can be referred
conveniently if they are filed in a systematic manner and a proper index is maintained for various
files.
2. Safety of Records:
Filing ensures the safe storage of records of different types. Letters and other documents are put
into folders and the folders are kept in cabinets. Thus records are saved from unforeseen
happenings like theft fine etc.
3. Documentary Proof:
Records serve as documentary evidence in case of disputes. Copies of records can be produced to
settle the claims with different parties. Records can also be produced in a court of law as evidence
when a party to the dispute resorts to the process.
4. Prompt Handling of Correspondence:
Filing enables the handling of correspondence properly without any delay. It builds up the
reputation of the organization and helps in securing orders.
5. Statutory Requirements:
Records are kept in compliance with provisions of various statutes like companies Act, Income tax
Act, Factories Act, etc
12
6. Barometer of Progress:
Filing makes available the records of previous years. It helps in comparing the current year‘s
performance with the previous years. Thus it is an important aid in measuring the efficiency of the
enterprise and various departments.
7. Decision Making and Policy Formulation:
Availability of up-to-date information is essential for taking important decisions and for
formulating policies.
8. Increased Efficiency:
Filing increased the efficiency of the office. It makes available to the management the required
information with speed and accuracy which is helpful for prompt decision-making. Follow-Up
actions are also taken quickly if records of the past correspondence are easily available.
1.7.4 Characteristics of a Good Filing System
1.
Simplicity: The system should be simple so that the employees concerned may operate it
without any difficulty.
2.
Accessibility: The system should enable files to be easily located and papers to be
inserted in files without disturbing the arrangement.
3.
Compactness: The filing section should occupy reasonable space in view of the cost
implication of large space.
4.
Economy: The cost of installation and operation of the system should be proportionate
to the benefits derived from it.
5.
Flexibility: The system should be capable of expansion as the activities of the
organisation expand.
6.
Safety: The records should be safe and available whenever they are needed. There
should not be any danger regarding insects, rain and mishandling.
7.
Retention: There should be a well-defined policy of retaining or discarding the papers
and records. Dead material must be discarded periodically.
8.
Classification: Most suitable method of classification should be adopted. Too many
miscellaneous files and bulky files must be avoided.
1.7.5 Centralized Vs Decentralized Filing
The document and records concerning a particular department of the business enterprise
can be filed either at the department itself or in any other central place. Thus, a business
enterprise can have either a decentralized or centralized filing system. Each system has its own
merits and demerits.
13
Centralized filing system is one where all the filing equipment and personnel are located in a
single section. In other words, under centralized system, all the records of the business firm
(relating to activities of all the sections or departments) are filed in one place or in the central
office. This place is usually called as filing section. This system implies that individual
departments have nothing to do with the filing of records.
Decentralized or Departmental Filing: Under Decentralized filing system, filing is done in
each individual department independently. In other words, each department makes its own
arrangements for filing, install separate equipment and the department staff themselves will look
after this work. Therefore, filing equipment are installed in each and every department. Hence, it
is also known as department filing.
Table Showing Difference between Centralized and Decentralized Filing
Merits of Centralized Filing
Merits of Decentralized Filing
1. There is no duplication of filing equipment
and work
1. Saves time in filing and obtaining . records
when departments are not located nearby.
2. Better utilization of storage space is possible
2. Departmental secrecy can be maintained.
3. There is saving in the cost of records
management
3. Specialized knowledge of staff about the
department prevent errors in filing.
4. Ensures uniformity and standardization of
filing operations. Hence greater efficiency
4. There is flexibility as regards time of using
and returning records
5.Trained personnel with specialization lead to
increased efficiency
5. Ensures prompt availability of records.
6.There is better supervision and control by
expert supervisors.
6. This is not possible
Demerits of Centralized Filing
Demerits of Decentralized Filing
1.Lack of specialized departmental knowledge
of the operating staff
1. Duplication leads to increased cost of
equipment and records.
2. There may be great delay in records being
made available to departments when they are
not located nearby
2. Lack of specialization of personnel in filing
work.
3.Strict rules regarding use and return of files
may cause inconvenience to departments.
3.Standardisation and uniformity filing work is
not possible when each department is free to
adopt its own system of filing.
14
4. It may be difficult to operate a centralized
filing system if records are frequently needed
by many departments.
4. Expert supervision is lacking.
5. It is difficult to maintain secrecy.
5. Confusion may arise in filing documents
concerning more than one department.
1.7.6 Methods Of Filing
(A) Old Methods of filing : There are old filing methods like spike or wire file, folder file,
pigeon hole file, box file, guard book file, expanding case file, and arch leaver file.
1. Spike or Piller and Post File: A thick steel wire with one sharp end and a wooden, plastic or
steel round at the other end is used for filing. It is placed on a desk or is hanged on a nail fixed
on the wall after filing is done.
2 Folder File : There are covers of card board or thick paper fitted with metal hinges for
fastening the papers together. A separate folder is allotted to each customer. All the letters
relating to that customer are kept in the file date wise. The papers are punched and then inserted.
The papers lie flat one above the other. These folders are placed horizontally in drawers.
3.
Pigeon Hole File: It is a special almirah or cupboard divided into number of small
compartments. It is open from one side and the compartments are square holes called ‗pigeon
holes‘. Each pigeon hole bears a letter of the alphabet. When letters are received they are sorted
according to the alphabet or subject wise. For example the letter received form Tushar & Co. is
inserted into the hole marked with ‗T‘. Brief particulars are also recorded on each letter. This
recording is known as docketing. This method is used in post office for sorting letters.
4.
Box File: Box file, as the name suggests, is made in the shape of boxes. Quite often papers
are first put into folders and then they are placed in box file. It helps to preserve papers better as
they are safe and gather less dirt.For classification purposes, papers relating to different subjects
can be folded. This method is useful for travelling agents and where correspondence is stored
temporarily.
5.
Guard Book File: Under this method, the paper or vouchers are pasted in bound book
datewise. This method is often used for recording minutes and preserving receipts and vouchers.
It avoids the possibility of loss or misplacement of any paper.
6.
Expanding Case File: Under this method, the papers are usually placed alphabetically in
numbered or lettered pockets of cases. This equipment is useful for filing papers in transit.
15
These cases or pockets can be useful for keeping papers together for temporary purchases.
These cases can expand as per the need.
7.
Arch Lever File: These are strong card board folders containing strong metal arches. These
arches can be operated by a lever. When a paper is to be filed, it is punched with two holes with
punching machine. The lever is then moved upward which opens up the metal arches or springs.
After paper is inserted through the holes the lever is pressed down to close the spring. The
papers in the file lie flat one upon the other.
(B) Modern methods of Filing
Old methods described above have limited use and are suitable only for small concerns. Even
then these are being replaced by modern methods. The modern methods of filing used in offices,
big or small, may be classified into two categories:
i) Horizontal Filing
ii) ii) Vertical Filing
Horizontal Filing: In this system papers are kept in file covers or folders one upon the other in
horizontal position. The papers are kept in chronological order inside cardboard file covers. The
papers are held together by metal hinges or levers. The files are then kept in cupboards in a
horizontal position one above the other. When any paper is required, the relevant file is taken
out and after use it is put back in the same position.
The advantages of horizontal filing are:
This method is simple to understand, easy to operate and economical to maintain.
Letters can be referred to in a file without removing them from it.
As letters are chronologically arranged, it becomes very easy to locate them.
Files are well protected from dust and moisture using thick covers and cupboards
Some of the disadvantages are:
It is not very flexible.
It is difficult to remove papers from files lying at the bottom or middle of the heap.
This system cannot be profitably used by large offices.
The equipments used are more space consuming.
Vertical Filing : This is the most modern method of filing. In this method papers are placed in
files and kept in an upright, standing position. The folders are stored in specially designed
cabinets. The front side of the folder is slightly shorter. The extended part of the back is used to
indicate the code number of the file. The drawers of the steel cabinet are deep enough to hold the
folders in vertical position. In order to divide the drawer into convenient sections guide cards are
16
placed at appropriate places. Under this method a separate folder is provided for each customer or
subject. The folders may be arranged alphabetically, numberically, geographically or subject-wise.
This system has become very popular in large offices and big business houses.
Advantages of vertical filing are :
It is a flexible system .
It is adaptable to various systems of classification.
The location of papers is possible without much difficulty and loss of time.
It takes less time to file papers in folders.
It provides proper safety of papers and documents.
Disadvantages of vertical filing are :
The equipment used like steel cabinets etc. is more costly.
It is not suitable for small offices.
Folders may slip down the drawers and get misplaced.
1.8 CLASSIFICATION OF FILES
Classification can be defined as the process of selecting headings under which documents are
grouped or classified on the basis of certain common characteristics before filing takes place. The
principal object of classification of files is to ensure prompt availability of information whenever it
is needed. Classification aids the filing functions to attain these principal objects.The efficiency,
particularly, the accessibility of a filing system depends largely upon the care with which
documents are classified. By classifying similar paper or papers belonging to a particular head or
subject, office staff are able to trace out the paper or documents required at any time with minimum
delay and trouble
1. Alphabetical Classification
2. Numerical Classification
3. Geographical Classification
4. Subject Classification and
5. Chronological Classification.
1. Alphabetical Classification:
Alphabetical classification is based on the occurrence of the letters in the alphabet as it is done for
the dictionary. Under the alphabetical classification, the filing of papers and documents is either by
17
the names of the correspondents or the subjects. This method of classification can be used in
correspondence filing, contracts, orders and staff records.
2. Numerical Classification
Under this method, each folder or record is given a number and the files are arranged in the
numerical order i.e. each customer or subject is allotted a number. All papers relating to a particular
customer or supplier or subject are placed in one folder bearing its distinctive number.
Folders are arranged in the cabinet numerical sequence and guide cards are used to divide them into
suitable groups of 10 or 20. Thus, if a customer, is allotted the number 14, all papers and documents
connected with him will be found in folder number 14..
3. Geographical Classification
Under this system, files are arranged according to the location or addresses of the persons or parties
to whom they relate. The classification can be street-wise, town-wise, district-wise, state-wise or
country-wise. This system will operate efficiently only when it is combined with either numerical
system or alphabetical system. This system of classification is generally followed in organizations
engaged in export trade or doing business over a wide geographical area. Mail order houses, banks,
insurance companies etc. also adopt this system of classification. This system is also suitable in
those concerns where records are required according to the sales territory.
4. Subject Classification:
Under this system, all documents concerned with a particular subject are brought together in one
file. Such document may have come from different sources and from different people. This system
is adopted only when the subject or content of a letter is more important than the name of the
correspondent. Each subject matter is kept in a separate file. These files may then be arranged
alphabetically, numerically or on some other basis. For instance, separate files may be maintained
for purchase quotations, purchase orders, income tax returns, traveling allowance bills and so on.
5. Chronological Classification
Under this method various records are identified and arranged in strict date order and sometimes
even according to the time of the day. It is a useful method for filing invoices and other vouchers
associated with accounts.This system may be useful if used along with some other system. The
records may be arranged alphabetically first and then can be arranged date-wise within each folder.
So this system cannot be used independently.
18
1.9 INDEXING
Indexing is an important aid to filing. Filing and indexing are so interrelated that filing without
indexing is incomplete and indexing without filing does not exist. Indexing means an arranged
system through which the required documents and papers are easily located for the speedy
disposal of urgent and/or ordinary matters.
Indexing is the process of determining the name, subject or other captions under which the
documents are filed. Index is a guide to records. The main purpose of an index is to facilitate the
location of required files and papers. Index helps the staff to find out whether a particular file
exists for a party or subject, and its place in the container. It also facilitates cross referencing.
Where records are classified in numerical order, or subject wise an index is necessary.
1.9.1 Purpose Of Indexing
Easy location of files and documents
Speedy cross-referencing
Saving of time and effort in locating records
Efficiency of record keeping
Reducing the operating cost of records management
1.9.2 Essentials Of A Good Indexing System
1. Simplicity: An indexing system should be simple to understand and operate. It should not
involve unnecessary complex in operation.
2. Economy: It should be economical in terms of money, space, and effort. The purchase of
indexing equipment requires heavy investment during initial period. Therefore, proper attention
should be devoted to ensure economical use in the end.
3. Flexibility: The selected index system should have sufficient scope for expansion. A single
system may be used for several purposes.
4. Efficiency: Any index system should ensure speed in operation and requires minimum time for
operation.
5. Safety: The index system should protect the records against dust, fire, water, rats, insects, water
etc. The safety should be equipped with lock facility to prevent pilferage of records.
6. Conformity with Filing System: The selection of index method depends upon the nature and
type of filing system adopted in an organization. Hence, there must be a correlation between the
19
filing system and index method.
7. Cross Reference: There should be Cross reference under the head under which a document
could be filed but has not been filed.
8. Signaling: A tab or slip should be attached at the edge of the card or file. The tab or slip
contains facts of the document briefly. This is used to draw the attention of the needy persons of
files.
19.3 Types Of Indexes
The main types of indexes are:
1.
Ordinary Page Index
a)
Bound book index
b)
Loose leaf index
c)
Vowel index
2.
Vertical Card Index
3.
Visible Card Index
4.
Strip Index
5.
Wheel or Rotary Index
1.
Ordinary Page Index: It is similar to the subject index given at the end of standard
books in which the subject matter is alphabetically arranged and then relevant page numbers
are given against each heading or sub-heading. Some times it consists of specially designed
pages fitted with a tab indicating an alphabet and on each page the names or subjects starting
with that alphabet are written along with the page numbers. This type of index can be (a)
Bound Book index, (b) Loose Leaf index, or (c) Vowel Index.
(a)
Bound Book Index: Under this system, index is prepared in a bound book or register
divided into alphabetical sections in which the names or documents are entered. Each section
has the leaves cut away at the right hand side so that the initial letters of all the sections are
visible at a glance. All entries relating to a letter or alphabet are arranged in the same section or
page reserved for it.
The merits of this method are:
It is a very simple method of indexing;
No special training is required of the staff;
It is very economical as it does not need costly equipment.
20
It is compact and handy and can be used for a long period;
It is popular in small organizations.
The main drawbacks are :
It is not flexible and cannot be expanded beyond a limit;
Alteration is not possible if anything has been wrongly entered.
Dead subjects cannot be deleted;
The location of names is difficult as they are not entered in alphabetical sequence;
It is suitable for small offices only.
(b)
Loose-Leaf Index: This is an improved version of the bound book index. The bound book
becomes inconvenient to handle if it is too big. In loose leaf index single sheets are punched to
fit in between metal hinges with the help of a metal screw. Pages are loose so that any page can
be taken out or additional pages inserted. To insert or remove the pages the metal hinges have to
be unscrewed. The binder with the loose index sheets can be locked so that no one can take out
any sheet without having authority to do so.
The main advantages of loose-leaf index are :
This method provides for maximum flexibility and can be adapted to suit the needs.
It is convenient to handle and provides quick and easy reference.
Dead records can be withdrawn and stored at the back. (iv) It is more economical than
other methods of indexing.
The sheets can be used for many different purposes such as keeping additional
information regarding a customer e.g. credit rating, telephone number, postal and
telegraphic addresses etc.
The main drawbacks are:
It takes longer to locate a particular index page.
Through constant handling the sheet may be damaged.
There is a possibility of the sheets being misplaced after they have been taken out.
If pages are used for multiple purposes, there are chances of committing errors.
(c)
Vowel Index: It is a modification of the book index. In big organisations which deal with
large correspondence, the index book is maintained on the basis of vowel classification in
order to facilitate quick reference. The section of book reserved for an alphabet is subdivided
21
into subsections, each of which is reserved for a vowel, that is, a,e,i,o,u and y. The page is first
selected by the initial letter and then by the vowel occurring after the initial letter, For
example, the name ‗Gandhi‘ will be recorded in the section reserved for ‗G‘ and in the vowel
sub-section ‗a‘. The system is simple, easy to operate, economical, and suitable for large
organisations. but it is not suitable for small offices.
2. Vertical Card Index Under this system each subject, customer or document is allotted a
separate card on which necessary information appears. The cards may be of small size (12.5
cms x 7.5 cms) or as per need. They are classified and arranged alphabetically, numerically,
geographically or subjectwise. The alphabetical classification is more popular. In some cases
more than one card may be prepared for the same set of information and each card may be
arranged in different manner e.g. in library usually two cards are prepared for each book — one
is arranged on the basis of author and the other on the basis of title of the book. The cards are
filed vertically in steel or wooden drawers. A hole is punched into each card to keep the card in
its proper place. Guide Cards may be used to indicate groups of cards in a class. This type of
index is very popular in big offices.
Advantages. (i) It provides for flexibility as the number of cards can be increased or decreased
without disturbing the arrangement. (ii) It is economical to operate (iii) It is simple and easy to
understand. (iv) The system can be used for many different purposes. (v) Dead records can be
withdrawn at any time. (vi) It can be used by several persons at the same time. (vii) Cards can
be arranged in any order.
Limitations. (i) All the cards are not visible at a glance. (ii) Cards may get lost or damaged
since removal of cards is easy. (iii) Cards may get torn due to constant handling. (iv) The
equipment is costly. (v) A regular check is required to ensure that cards removed for reference
are replaced in their proper places.
3. Visible Card Index
The cards are arranged flat in a shallow tray or metal frame. Each card is attached to metal
hinge and overlaps the one before it, so that name address and other particulars are visible
without touching other cards. The frames or trays are attached vertically to the metal stands or
they can be put horizontally into cabinets. The details of data can be written or typed on the
front or back of the cards for reference.
22
Advantages : (i) It occupies less space. (ii) The reference is much faster. Cards are easily
located. (iii) any information can be added without disturbing the arrangement. (iv) Out dated
cards can be removed easily whenever necessary. (v) Its capacity is quite large. More cards can
be accommodated in the same space. (vi) It is widely used in libraries, banks, insurance
companies and other organisations.
Disadvantages. (i) It requires costly equipment. (ii) Designing and operating the system needs
Commerce (Business Studies) training. (iii) Making entries on cards takes more time.
4. Strip Index:
In every office there is need for a list of names of parties to be maintained with their telephone
numbers, addresses etc. A line entry on a narrow strip of card board can be prepared for a single
item. These strips are arranged in a frame in such a way that they can be taken out and replaced
with ease. Frames can be hanged on the wall or put on the table in a book form or even arranged
on a rotary stand which can be turned round to look at any part of the index.
5. Wheel or Rotary Index:
Under this method cards are arranged around the hub of a wheel which may be portable. A
single wheel can hold as many as 5000 cards. A card can be inserted or withdrawn without
disturbing the other cards. Entries can also be made on the cards without removing from the
wheel. The merits of this system are quick and easy referencing, economy of time and efforts,
economy of space, elasticity, etc.
1.10 FILING EQUIPMENT
Individuals and businesses have a variety of choices when it comes to filing equipment. Some
options offer high levels of security while others can accommodate a high density of files. The
amount of space you have, the sensitivity of the files and your preference for physical or
electronic records all influence your choice of filing equipment.
1.10.1 Purpose Of Selecting Filing Equipment
The following purposes must to keep in mind while selecting the filing equipment.
1. It protects the document against careless handling.
2. It prevents theft or unauthorized references.
3. It protects the documents against deterioration through dust.
4. It reduces the physical efforts in inserting, locating and extracting documents.
23
5. It protects the documents against the loss made by fire.
1.10.3 Factors Affecting The Selection Of Filing Equipment
The following factors are affecting while selecting anyone of the filing equipment.
1. The number and the size of records to be maintained.
2. The frequency of reference of files.
3. The speed with which the documents is required.
4. The physical appearance of the equipment as a piece of furniture.
5. The life of filing equipment and the duration required for maintenance.
1.10.2 Requirements Of Good Filing Equipment
1. Adequacy: The filing equipment should be fully adequate for the purpose for which it is to be
used. If not so, the labour of filing and expends will be increased.
2. Simplicity: The filing equipment should be simple with adequate indexes, guides and folders.
3. Less effort: The use of filing equipment should require less effort.
4. Quality: The duration of the filing equipment should not be less than 20 years. The frequent
changing of filing equipment may dislocate the documents and increase the expenses.
5. Economy in Space: The filing equipment should be economical in its use of space.
1.10.4Types Of Filing Equipment’s
Physical Filing Equipment
Filing Cabinets : Four drawers allowing files to be stored laterally is standard. These cabinets
keep records secure as these cabinets can be locked, a company can limit access to sensitive
files while still allowing employees and visitors to enter the room. Out of all the physical filing
equipment options, cabinets tend to be the most expensive and have the most limited capacity.
Open Shelving
An alternative to filing cabinets is open shelving. Units are similar to open bookcases and are
specifically designed for folder height and width. The design allows users easy access to files
and can be either stationary or be mobile if rollers are attached to the bottom. Open shelving
saves on space and money. Shelf filing equipment typically is three times less expensive than
filing cabinets. Compared to a four-drawer filing cabinet, a seven-tier open shelving system has
24
80 percent more capacity.
Digital Filing Equipment
Individuals and businesses that want to take advantage of technology can store files digitally
rather than physically. Electronic documents are saved directly into the system, and physical
documents can be scanned and converted into a digital format. Digital filing systems allow users
to search information quickly and keep data secure. As with physical filing, users have a choice
of systems and equipment for a digital system. Files can be organized and stored locally on a
laptop's or PC's internal hard drive.
External Devices
It's convenient to use a computer's internal hard drive to store files, but you risk losing your
information if the hard drive is corrupted or physically damaged. To mitigate this risk, users
may want to back up data to an external device. PC World recommends backing up critical files
to an external hard drive and using a thumb drive to transfer files as needed.
Servers
Businesses that want multiple parties to have access to the same data may want to invest in a
server. Servers act as a central repository for many users' files. PC World notes that businesses
can host multiuser applications like databases and enterprise resource planning systems on the
server. This makes it easy for a large number of individuals to have access to the same files.
Server data can be backed up to an external device or the cloud for extra security. Physical
servers look similar to a high-end PC. Alternatively, businesses can choose a cloud-based
hosting service Amazon Web Services, Windows Azure and Rack space Cloud Services are all
options which doesn't require a physical server filing cabinet that takes up a 6-foot-by 24-foot
filing area can hold approximately 8,448 folders.
1. 10.5 Steps in Installing Or Planning The Filing System
1. Preparation of List of Documents: A list of all documents and papers to be filed is prepared. The
list is prepared according to the needs and policy of the concerned business organization. Generally,
the list contains the documents to be filed which are required in future reference.
2. Decide Period of Storage: The period of storage of documents should be decided by the top
management after consulting all the departmental heads.
25
3. Decide Storage Space and Acquire: The need of storage space is decided by the office manager.
Keeping in view of volume of documents to be filed, adequate funds may be allocated to acquire
needed storage space.
4. Filling Department Layout: The layout of the filing is prepared in such a way that the documents
are accessible in an easily manner. The storage arrangement should be decided on the basis of the
frequency use of the documents.
5. Deciding Filing Equipment: Various types of filing equipment can be procured to preserve
different kinds of documents. The nature and importance of documents are taken into account to
select filing equipment. Fireproof filing equipment should be purchased to preserve valuable
documents and confidential records. The routine types of records are preserved in an open shelf.
6. Determining System of Classification: A suitable system should be selected for the classification
of records.
7. Protection of Records: Proper arrangements should be made in order to protect the records form
loss or damage.
8. Training of Staff: Adequate training should be imparted to office staff for handling various filing
operations. There must be a clear definition of duties and responsibilities of staff members of filing
department.
9. Issuing Procedure: No admission without permission principle is followed to enter into the filing
department. Besides, the files should be issued only to the authorized persons. A separate register is
maintained to record the issues and receipts of all files.
QUESTIONS
PART A
1. Define ‗Office‘.
2. List out the Basic Office Function.
3. Classify various types of offices.
4. Demonstrate the qualifications required for an office manager.
5. State the qualities of a good office manager.
6. Bring out the difference between traditional office and modern office.
7. Enumerate the advantages of filing system.
8. Differentiate horizontal filing and vertical filing.
9. Mention the purpose of indexing.
26
10. Determine factors affecting the selection of filing equipment
PART B
11. Describe the importance of office to an organisation
12. Elaborate the functions of modern office.
13. Discuss in detail about the functions of office manager.
14. Explain in detail the various functions and objectives of record management.
15. Describe the essentials of a good filing system.
16. Differentiate Centralized and decentralized filing system
17. Classify the various types of filing equipment.
18. Elucidate various types of classification of files.
References
1. Office organization and Management- By S.P.Arora.
2. Office Management- By P.K. Ghosh
3. Office Management – By Kathiresan &Dr.Radha

SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
UNIT – II - OFFICE MANAGEMENT– SBAA1407

1
II. MAIL AND MAILING PROCEDURE
2.1 MEANING AND DEFINITION
The term “Mail” in the common parlance refers to written communication. It may be either
received or sent out. A mail received is known as inward mail and a communication sent out is
called as outward mail. Mail may be described as any written communication which passes through
the messenger, courier or the post office. There is need of continuous contacts with the customers,
suppliers, branches, departments, banks, financial institutions, government agencies, non —
government organization, and the like.
George R. Terry rightly remarked that “it is doubtful that a modern office could exist
without mail”. The reason is obvious that every business house has to maintain close contact with
the outside world. It should correspond to its customers, its own branches, departments, and various
other institutions, government etc., the business firm grows; the volume of transactions will also
grow.
2.2 TYPES OF MAIL SERVICE
Business mail is of three distinct types. They are listed below.
1. Incoming or inward mail.
2. Outgoing or outward mail and
3. Inter — departmental mail.
The form of these types of mails are letters, documents. packets, parcels, telegrams, orders,
remittances etc. Prompt and correct handling of mail is necessary for achieving purpose of mail.
Moreover, proper handling of mail increases the goodwill of the business office. The existing
relationship of business office with outsiders is strengthened through efficient operation or handling
of mail service. Thus handling of mail is an important supplement to other office operations, viz.,
making original records, typing and duplicating etc. The mailing service should be planned and
organized properly to ensure prompt and correct handling of mail.
2.3 IMPORTANCE OF MAILING SERVICE
In the modern globalized business world, mail service is an integral part of office work. Hence,
adequate facilities should be provided for efficient and successful performance of mail service. An
efficient mailing service offers the following benefits.

2
1. It ensures continuous contacts with outsiders.
2. A good impression is created in the minds of outsiders and thereby improves the goodwill of the
business.
3. The interdepartmental co-operation is also improved with the help of efficient mail service.
4. It helps the business office in the creation of correspondence and record keeping of all the
departments.
5. It helps to reduce the cost of the mailing service.
6. The new employee of business office gets training very easily and makes them familiar with the
organizational set up, work routine, authority and responsibility, organization structure and the like
of the firm.
2.4 COMPONENTS OF MAIL SERVICE
The following elements are included in the efficient mailing service
1. Adequate facilities are provided for the mail service.
2. Creation and organization of mailing department correctly.
3. Arrangements made with post office.
4. Establishing inward and outward mail procedure.
5. Mechanization of mail service.
6. Supervision of mail service.
2.5 CENTRALIZED CORRESPONDENCE
A separate division or section or department is created for handling correspondence to the entire
organization under centralized correspondence. A separate person is appointed to organize and look
after the work of the correspondence department. The volume of correspondence is very large in
large organization; hence, a separate correspondence department is created and assigned to the
qualified person. He exercises full control on the department. The correspondence department
receives all letters, gathers the necessary information from various departments, drafts, letters and
replies, dictates letters dispatches them and follow up all letters. But at the same time, personal
secretary is dealing the letters of top executives of an organization. A correspondence manual is
prepared by the correspondence department for reference of all the departments
3
Advantages of centralized mailing service
The advantages of a centralized mailing department are :
i. High degree of specialization: It makes certain that specialization in the mailing service
is ensured. Specialization enables precision and rapidly in the work.
ii. Uniformity in standard: It maintains consistency in the standard of quality and approach.
This system ensures standardization of all correspondence made by the business hours.
iii. Better quality of work: It increases efficiency of work in their entails good output. As a
consequence the degree of work become better and the organisation attains a good
reputation.
iv. Better supervision and coordination : A well trained and expert supervision may be
appointed to lead the dispatching department. Better supervision would ensure an ever
and quick performance of mailing operations.
v. Saving time and money: Mailing operations can be methodical under this system. Proper
methods can be set forth and brought into union with mailing operations. This would
make for savings in time and money.
vi. Increase in efficiency: It increases efficiency of employees as they specialize in looking
after the correspondence only.
vii. Keeping away duplication of work: All types of corresponding (inward, outward and
inter department are changed to the central mailing department. As a result duplication of
endeavor is stopped.
viii. Use of modern equipment: The mechanization of the mailing dept, is possible under this
system. Various labor saving devices (folding and sealing machines, fracking machines
can be used in the best way.
2.6 HANDLING OF INCOMING MAIL
In every organization, there are defined steps for physical handling of inward mail so that the mail
could reach the concerned official without delay. These steps vary depending on the size and nature
of the organization. The following procedure is usually followed in handling of incoming mail if
the mail is received manually/physically.
4
1. Receiving Mail
Mail is delivered once or twice a day by a Postman in an organization while mail from special
messengers or courier companies keep pouring throughout the day. A Junior Secretary or Mailing
Clerk is entrusted with the task of receiving the mail and providing acknowledgement of the
receipt, wherever necessary. In case the mail is to be received from Post Box or Post Bag, a person
is deputed to collect the same from the Post Office once or twice a day.
2. Sorting Mail
After receiving the mail, it is necessary to sort the received mail so that mail marked as Private,
Personal, Secret, Confidential etc. are not opened. This type of mail is directly delivered to the
person concerned unopened. Important mail viz. court summons, tenders, confidential reports etc. is
sorted out from the routine mail to accord priority in opening. Routine mail consisting of sales
letters, catalogues, product literature etc. are opened at last. Trays or open racks with separate
compartments are usually available in Mailing Department in which segregated mail is kept while
sorting. Trays or racks used for sorting mail have the name of the departments clearly marked on
them.
3. Opening Mail
A paper knife is generally used for opening envelopes. In case of large mail, a Letter Opening
Machine is helpful as it improves efficiency and opens the mail neatly. While opening an envelope,
it should be ensured that:
a) contents of the envelope are not damaged.
b) before disposing off the envelope, nothing is left inside the envelope.
c) enclosures are fastened if they are not properly tagged.
Sometimes, it is necessary to preserve the envelope received along with the mail. In such cases, the
same is attached along with the letter.
4. Examining Contents and Stamping Mail
After opening the mail, a Secretary should briefly examine its contents. Examining of contents is
done to again sort out the mail which needs immediate action so as to accord priority. Sometimes,
there are certain letters which require time-bound reply and are to be dealt on urgent basis.
Examining of contents of mail also help to know if any of the enclosures of the letter are missing.
In such cases, the facts are recorded on the letter. All the mail received is date-stamped to
5
authenticate receiving of the same in the organization. It can be done with the help of a Rubber
Stamp or an Automatic Numbering & Dating Machine.
5. Recording Mail
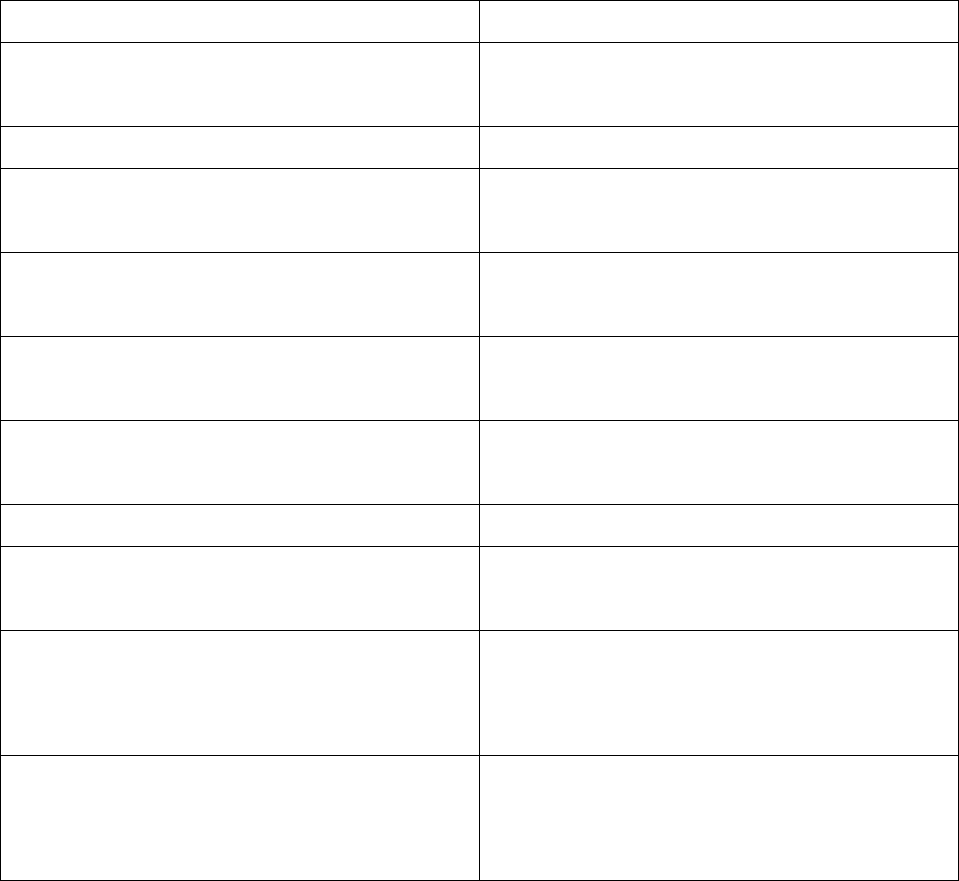
Recording of mail helps in tracing out any received letter at a later date. An Incoming Mail Register
is maintained to make a brief record of all the incoming mail. Incoming Mail Register is also called
Diary Register or Dak Register. An Incoming Mail Register also has a column viz. Date of Reply to
ensure that all the received mail has been attended to.
6. Distributing Mail
The recorded mail is segregated department-wise and immediately distributed to the concerned
departments by a peon or messenger.
7. Follow-up Action
Every incoming mail which needs a follow up action should be quickly attended to by the
concerned official. In business houses, it is ensured that every mail received should be disposed-off
within maximum 3-4 days, wherever possible.
2.7 HANDLING OF OUTGOING MAIL
Like incoming mail, speedy disposal of outward mail is equally important. Delay in sending mail
not only results in loss of business prospects but also creates a bad image for the company. While
on the other hand, quick replies of mail show the importance which has been attached to it. The
following steps are generally followed in case of handling of outward mail physically:
1. Production of Mail
The letters which are sent out of an organization are prepared and signed by an authorized person.
Every outgoing mail should bear a reference number which facilitates future reference of the same.
The mail ready to be dispatched is usually kept in „Out Tray‟ available in all departments.
6
2. Collection of Mail
All outgoing letters are collected twice a day by a peon deputed by Mailing Department for onward
transmission. A Professional Secretary should ensure that the mail is collected timely so that it
could be dispatched from the office without delay. It is also the duty of the Professional Secretary
to mention the preferred mode of dispatch of the mail. The Mailing Department or Despatch
Section delivers the mail according to the instructions given on the mail.
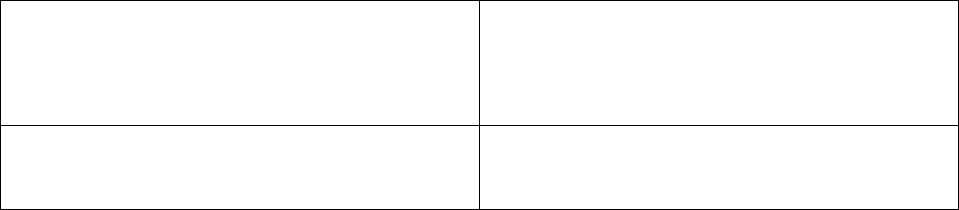
3. Recording Mail
Every outgoing mail is to be recorded in a register called Despatch Register or Mail Outward
Register. A specimen of the same is given below:
4. Writing of Addresses
If the mail is to be sent in an envelope, the same should be selected of suitable size
according to the size and number of paper (s) to be inserted it. While writing address on an
envelope, it is ensured that the address should be written parallel to the length of the cover and in
the lower half and towards the right-hand side thus leaving adequate margin at the top for the
postage stamps and labels, postmarks and other indications.
Writing of correct, legible and complete address of the receiver on the outward mail is very
important point to be taken care of by a Professional Secretary. Use of PIN code, speedy and
accurate postal delivery is possible all over the country. In case of addressing of large mail, an
Addressing Machine can be used which saves a lot of time and energy of a Professional Secretary
besides reproduction of correct address on the outgoing mail?
5. Folding letters and inserting them into Envelopes
Letters intended to be inserted into envelopes should be folded in such a manner that it has
minimum number of folds according to the size of the envelopes. Letters and enclosures must be
7
folded together. Folding and Inserting Machines can be used to make the task easy for a secretary in
case of handling of large outgoing mail.
6. Sealing of Envelopes
The next step is to seal the envelopes to secure the contents of letters. The mail containing financial
documents, registered and insured articles should be sealed carefully. Book Post mail mostly
consisting of Product literatures, catalogues, price lists etc. are sometimes not sealed for the
convenience of the receiver.
7. Affixing Stamps on Envelopes
On the outgoing mail to be sent through Post Office, postage stamps of required denominations are
to be affixed as per the prescribed rates. The mail is weighed to calculate the correct amount of the
postage stamps. Over-stamping and under-stamping are to be avoided at all costs. Franking
Machines are commonly used by offices for stamping the outgoing mail.
8. Posting Mail
Posting of Mail is the last step in the procedure of handling of outgoing mail. Letters intended to be
sent through Post Office are sent by a peon to the nearest Post Office. Mail marked as Registered,
Speed Post, Insured etc. are submitted at the counter of the Post Office and a proof of delivery of
the mail is obtained. Local mail which is to be sent through special messenger is handed over to the
concerned person along with Peon Book. Courier Mail is handed over to the representatives of
courier companies, whenever they arrive as per the specified time schedules.
2.8 HANDLING OF ELECTRONIC MAIL
Electronically, mail can be received or sent out with the help of computer, fax, mobile phone etc via
a network. This type of mail does not have any elaborate handling procedure. The mail is mostly
addressed by name on individual‟s e mail address or number. Fax and e-mail messages on receipt
are directly delivered to person concerned for further action. E-mail means messages distributed
from one computer to one or more recipients with the help of internet. An e-mail message consists
of two parts: the message header and message body. The message header contains space for email
address (s) and subject. The content of the mail is written in the message body. The mail is easy to
compose and transmit just with a click of button. It is generally received and sent from an
individual‟s e-mail address in an organization.

8
E-mail has given rise to concept of Paperless Office because of the following advantages:
• Speedy delivery
• Economy
• Security
• Feasibility of sending bulk mail
• Possibility of use of pictures, demonstrations etc.
• Automated record management
The problems which may be associated with e-mail include threat of virus, hacking of mail,
crowded in-box etc. However, with the various techniques, it is possible to deal and overcome all
these hazards. It is important that in-box of mail should be checked-in regularly. Due to exponential
growth of mail volumes, Digital Mail Rooms are set up now-a-days in organizations. In such Mail
Rooms, documents are scanned, archived and retrieved in original image format. Electronic mail
formats, fax etc. can also be combined while document processing. The setting of Digital Mail
Rooms has reduced decision making cycles, saved paper costs and rationalized circulation of
information.
2.8 MAIL ROOM EQUIPMENT
A mailroom is a room in which often incoming and outgoing mail is processed and sorted.. Various
mechanical equipment is used to handle the incoming and outgoing mail efficiently and effectively.
Use of the mechanical devices also help to reduce monotony and increase accuracy of mailing
operations. Equipment and machines in Mail Room has following advantages:
Increase in the speed of operations.
Saving of time.
Improvement in efficiency and accuracy.
Elimination of wastage.
Simplification of fixing of postage and avoidance of misuse of postage stamps.
The following Mail Room Equipment is commonly used in a large organization:
1. Letter Opening Machine
With the help of a Letter Opening Machine which operates manually or electrically at a great speed
and can open 100 to 500 letters per minute, work of opening of mail can be efficiently managed. It
has a rotary knife which shaves off a very thin slice of the edge of envelopes. While using the
machine, one should be careful that the contents of the envelope are not damaged.
9
2. Numbering and Dating Machines
An Automatic Numbering & Dating Machine is used for stamping on the incoming mail. In this
machine, the next serial numbers and date automatically changes after every use with the help of
self-inking stamp pad.
3. Folding and Inserting Machine
A Folding Machine can fold approx. 5,000 to 10,000 sheets per hour. It is possible to fold and insert
letters into an envelope with this machine. The machine is to be adjusted as per the required number
of folds according to size of envelope.
4. Sealing Machine
Sealing Machine helps in automatically moistening the flaps of an envelope and then sealing the
same. Sealing with wax can also be conveniently done with the help of this machine. Hand operated
sealing machines can seal about 100 envelopes a minute while electrically operated ones can
operate at a speed of 15000 envelopes in an hour. The work of sealing of mail can be performed
very neatly and efficiently with the help of this machine.
5. Mailing Scale
A Mailing Scale is used to weigh outgoing mail and ascertain postage stamps which are to be
affixed on it. Digital scales at a very economical price are widely available in the market. It is an
essential equipment in Mail Room for performing mailing operations.
6. Addressograph (Addressing Machine)
The help of such a machine is taken when frequently letters or circulars or notices have to be sent to
the same addressees. For example, communication to members of an association or company,
electric or telephone bills to subscribers, premium notices to insurance policy holders, etc.
It helps in printing of addresses on envelopes, parcels etc. The machine is used when mail is to
be sent to those customers which are regular and frequent on mailing list. It can be operated
manually or electrically. In this machine, there is a ribbon to give print of the addresses from
already prepared embossed plates. Once the address plates are prepared, it can be repeatedly used
any number of times. The required plates are selected and fed into the machine from one side. After
operating the machine, one can get the addressed envelopes from the other side.
(a) It has tremendous speed of operation,
(b) There is no mistake in printing the name and address,
10
(c) The operation is simple,
(d) It can be used for a number of purposes and in a number of ways,
(e) It leads to economy.
It has disadvantages too:
(a) The metal plates are costly though durable,
(b) It is difficult to make alterations.
7. Franking Machine
This is a machine used for printing on envelopes, cards, etc. designs of postage stamps of different
denominations, showing the date, amount, the place of stamping, and the registered number of the
user. In addition, an advertisement slogan also may be printed. Commercial houses, educational
institutions, Government offices, and various other organisations commonly use such machine
instead of using ordinary adhesive postage stamps. This machine has been introduced after the
International Postal Convention of 1922. Such a machine can be purchased or hilled but has to be
taken to a post office for registration and a licence.
A number is allotted by the post office to the user. There is a meter attached to the machine
showing the amount of money consumed by way of postage. An amount, based on the probable
consumption has to be estimated and paid in advance to the post office.Accordingly the post office
adjusts the meter up to that limit, locks it and seals it. The user can use the machine until that limit
of postage value is reached and after that the machine stops to operate. Again the machine has to be
taken to the post office for new adjustment of meter on payment of money in advance.
In order to do the franking the following steps have to be taken:
(1) The letters have to be sorted according to the amount of postage required for them.
(2) The machine is adjusted with one denomination at a time. For example, 25 paise, 35 paise, and
so on. Letters requiring 25 paise stamp shall be franked at a time. Then letters requiring 35 paise
stamp and so on.
(3) For envelopes or articles of heavy thickness which cannot be entered into the machine, separate
sheets are franked and then pasted on the articles.
(4) If there is any mistake such an envelope is preserved and can be deposited with the post office
for refund.
11
(5) Every day the date printing mechanism has to be adjusted.
(6) The machine must be kept under the charge of a responsible person so that there is no misuse.
Advantages:
(a) The operation makes saving of time. About 2,000 letters can be franked in an hour by a hand-
operated and 15,000 by an electrically operated machine.
(b) A stock of postage stamp has not to be maintained.
(c) Pilferage of postage stamps can be avoided.
(d) Printing of advertising slogans is a cheap method of advertising.
Disadvantages:
(a) There may be wastage through franking of wrong amounts.
(b) The mail has to be carried to the post office every day after franking and cannot be dropped in
post box.
(c) There may be misuse of the machine.
(d) Loose stamps still may be necessary for urgent letters which have to be posted immediately but
by that time post office has closed.
(e) A good amount of money has to be paid to the post office in advance.
(f) It has operating and maintenance costs.
2.9 POSTAL SERVICES
Effective and efficient handling of all incoming and outgoing physical mail reflects efficiency of a
Secretary. Post Office, Special Messenger and Courier Companies help in physical delivery of mail
from one place to another. Post Office provides various facilities regarding domestic and
international carriage of mail. Local mail of urgent nature may be sent with the help of a Special
Messenger. Sending mail by this mode ensures quick delivery of mail along with its
acknowledgement. Now-a-days, Courier companies are also playing a vital role in delivery of mail
due to various additional services they are offering to their clients. This has also become a popular
mode of delivery of mail, whether local or international. However, today, the most frequent method
of sending and receiving mail is electronic mail (e mail).
Post Box : A post box is a uniquely addressable lockable box located on the premises of a post
office. Generally, post office boxes are rented from the post office either by individuals or by
12
businesses on a basis ranging from monthly to annual, and the cost of rent varies depending on the
box size Only fully prepaid unregistered mail namely letters, inland letter cards, postcards,
registered newspapers, books, or the post bearing the Post Box No. are delivered through post box.
Value Payable Post: The value payable system is designed to meet the requirements of those
persons who wish to pay for articles sent to them at the time of receipt of the articles and also to
meet the requirements of traders and others who wish to recover the value of article supplied by
them through the agency of the Post Office.
Speed Post : Speed Post is a very high speed express service for letters and documents with time-
bound delivery across the nation and around the world. Speed Post offers a money-back guarantee,
under which the Speed Post fee will be refunded if the mail is not delivered within the published
delivery norms.
Opening a Corporate Account:
For corporate customers and regular users, India Post provides many value added services
including pick-up from the premises, convenient monthly billings, account management facilities,
assistance in import/export procedures of shipments, corporate tracking facilities, volume discounts
etc. When we open a corporate account, we open the door to convenience and customized solutions,
as per our requirements.
Surface Air Lifted (SAL):
Surface Air Lifted (SAL) is one more premium mailing service from India Post. SAL mail is faster
than sea mail yet cheaper than air mail - an ideal combination of air and surface transport for quick
and economical mail deliveries. SAL mail will be Air Lifted between the country of origin and
destination. However within the country of origin up to the office of exchange and in the country of
destination from the office of exchange to the point of delivery, SAL mail will be transmitted by
surface.
2.10 COURIER SERVICES
Due to features viz. high speed, security, tracking, acknowledgement and committed delivery
schedules, courier services have witnessed a phenomenal growth in modern era. Courier services
are popular among the business organizations as they offer the following solutions to the customers
in regard to mail delivery:
Delivery of any type of article of any value or weight. (e.g. perishable commodities,
medicines etc.).
13
Reliable and safe delivery.
Speedy delivery as they follow stringent time schedules.
Wide coverage (almost all corners of globe).
Transit insurance facility.
Facility of consignment status by web based Track and Trace System which can be had on
mobile and e-mail.
Proof of delivery on request.
Maintenance of quality standards.
Provision of logistic solutions like go-down facilities, packing etc. as per customer‟s needs.
Processing of mass mail (envelope labelling in case of product promotional literature,
sending of greetings etc.)
The world's largest courier companies include DHL, FedEx, OBC Express Ltd., UPS, etc.
QUESTIONS
PART A
1. Differentiate between Electronic Mail Handling & Physical Mail Handling.
2. List various mailing services.
3. Discuss the importance of mailing service.
4. Enumerate the Advantages of centralized mailing service
5. Discuss the use of Franking Machines
6. Describe the procedure for handling emails in an organisation
7. State the advantages of using equipment and machines in mail room.
8. Outline the significance of addressograph.
9. Elaborate the components of an efficient mailing service
10. Explain centralized correspondence.
PART B
11. Discuss the procedure for handling inward mail.
12. Outline the procedure of physical handling of Outgoing Mail
13. Explain various mechanical devices commonly used in the mailing section of an office.
14. Describe facilities given by Department of Posts regarding carriage of mail
15. Explain various services which may be provided by courier companies to their clients
16. Summarize advantages & disadvantages of Centralized mailing system.
14
References
1. Office Management ByDr. P.K. Ghosh
2. Office Management ByKathirasen and Dr.Radha
3. Business Communication ByUrmilaRai and S M Rai

1
SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
UNIT – III - OFFICE MANAGEMENT– SBAA1407
2
III. MODERN OFFICE EQUIPMENTS
3.1 OFFICE AUTOMATION
The history of modem office automation began with the typewriter and the copy
machine, which mechanized previously manual tasks. However, increasingly office
automation refers not just to the mechanization of tasks but to the conversion of information
to electronic form as well. The advent of the personal computer in the early 1980s
revolutionized office automation. New electronic procedures and systems becoming more
and more popular in modern Automated Office which otherwise called as “Paperless Office”.
A „Paperless Office‟ is one in which paper has been replaced by electronic, digital,
micrographic and micro processing systems. This Paperless Office incorporates voice inputs,
word processing, optical character recognition, electronic mail, calendars, message sending,
filing directions and text editing, computer indexing and processing, telecommunications and
colour graphics systems into a fully automated office facility. Several Modern Offices
provide satellite communication video teleconferences, electronic mail and computer-to-
computer hook-ups for intra-company use. This chapter focuses on office automation and
various modern equipment used in modern office.
Automation may be described as usage of advanced technology with the help of
specific devices of communication and control in self-regulation without human intervention.
It can also be termed as application of information technology to the typical clerical and
secretarial tasks such as communication, correspondence, documenting and filing. In simple
words automation means “Creation and application of technology to monitor and control the
production and delivery of products and services”.
Office automation is the use of various technologies to simplify and support routine
office functions, improve communication, increase office productivity and enhance the
quality of clerical output. Many office tasks including preparation of reports and
correspondence, communications, file maintenance, duplication and distribution of written
materials, can be facilitated and improved through word processing and other office
automation techniques.
3
3.2 OFFICE MECHANIZATION
Mechanization means the process by which machines and equipment‟s are
introduced with a view to speeding up the administrative process.
Office cost is reduced substantially by the introduction of machines.
The introduction of mechanization leads to saving in time and reduced operational
costs.
3.2.1 Objectives of Office Mechanisation
1.
Savings in Labour
This is the main reason for installing many machines in an office. If a machine saves
labour, it is possible to turn out more work in a given time than before the machine was
used. Savings in labour results in a reduction in pay roll expenditure. In simple words, a
machine should be capable of avoiding the salary expenses payable to five or six clerical
staff.
2.
Savings in Time
Savings in time is another major advantage of mechanisation. The use of machine is
invaluable for jobs, which have to be completed within a specified time. Examples are
preparation of wage sheets, dividend warrants etc. The value of some machines, in fact
lies in that feature alone.
3.
Promotion of Accuracy
Mechanisation ensures accuracy. The machines give a mechanical accuracy and save
much labour time in checking back as well as the possible annoyances caused by errors.
However, human error in operating the machines can still create problems. As such the
men operating the machines should not commit any mistake.
4.
Minimizing the Chances for Fraud
Sometimes, machines are installed though they do not save labour or time, but due to their
intrinsic value in minimising the opportunity for fraud. A good example of such a
machine is the cheque-writing machine. It is used in offices even when the number of
cheques to be issued is quite small.
4
5.
Avoidance of Monotony
Some kind of work is so monotonous as to constitute drudgery. In those cases, office
machines have special value in helping to eliminate distasteful work These machines will
relieve the employees from monotony and boost up their morale. Such machines will
provide considerable satisfaction to them
6.
Provision of Service at the Whole Organisation
Very often mechanisation shall be considered as economically viable because the services
of a single machine are made available to the organisation as a whole rather than to a
single department.
7.
Services Beyond Human Capacity
Some large machines perform two or more operations simultaneously. For instance, large
accounting machines write figures, add them up at the same time and then move the paper
ready for the next. In addition, by the use of carbon papers, several documents can be
written, with identical information at one posting. This, of course, may be done manually
but machines create as many twenty copies of a document simultaneously. Analysis can
be obtained at the time of entering in ledger accounts. These things are in fact beyond
human capabilities.
8.
Efficiency in Performance
From the management point of view, greater control is possible and more information in a
condensed form will be made available to them as quickly as possible. Hence, it can take
prompt decisions. Prompt decisions are essential to meet the business challenges of the
present day. All these factors will ensure greater success to the company in achieving its
cherished goals.
9.
Uniformity of Office Records
The records of the office will become uniform with the use of machines and give a better
appearance. Moreover, mechanisation facilitates standardisation of office routines and
procedures and therefore a better co-ordination of work
5
3.2.2 Advantages of Office Mechanization
1.
Quality of Work
The work performed with the help of machine is generally more neat and legible than the
work completed by hand. Therefore, the using of machines ensures the quality of work.
2.
Low Operating Costs
Only labor and time saving machines are used in an office. Therefore, the wage bill may
be reduced and produce more work.
3.
High Efficiency
All the work can be performed with short period. In this way, the machines are utilized to
increase the efficiency of operations.
4.
Accuracy
Human beings may commit more number of errors knowingly and unknowingly.
However, the mechanization prevents such clerical errors and omissions. It improves
accuracy of work, especially in accounting, computations, and statistical calculations.
5.
Relieves Monotony
Using machines and equipment can reduce boring and time consuming. The monotony of
doing a work is avoided in this way.
6.
Standardization of Work
The work of office routines and procedures can be standardized with the help of
mechanization facilities. The standardization leads to uniformity and better coordination .
7.
Effective Control
More information can be supplied quickly to management. The management also
exercises effective control. Thus, the chances of fraud are minimized.
8.
Create Goodwill
The improved efficiency leads to greater profitability and creates goodwill of the
organization in the minds of suppliers and customers who are dealing with the
organization.
6
9.
Quality Decision
Mechanization supplies adequate information to the management without any delay. This
process facilitates the management to take quality decision.
10.
Covering More Work
A single machine can do the work of two or three employees. Hence, the employees may
be deputed to do some other work. In this way, more work can be covered through the
process of mechanization.
3.2.3 Disadvantages of Mechanization in Office
1.
Heavy Investment
The initial cost of a machine is high. If number of machines purchased is greater, there is
a need of making heavy investment by the management.
2.
Waste
An idle machine is a waste. This wastage is greater, if the machine is costly.
3.
Retrenchment Problem
Adoption of certain machines will lead to retrenchment of some employees. If so, the
management will face such problem.
4.
No Trained Staff
The purchasing and utilization of machines require skilled employees for operation. If
trained or skilled employees are not available, the machines cannot utilize properly.
5.
Increase Cost of Operation
Sometimes new staff may be appointed to operate the machines. If so, the salary bill of an
organization will be increased. Thus, there is an increase in cost of operation.
6.
No Power No Work
Most of the machines are operated with the help of power. There is no possibility of doing
a work during the period of power cut or power failure.
7.
Break Down of Machine
The machines may be break down over a period. There is stagnation in the performance
of work if machines are break down.
7
8.
Set Right the Machines
The outsiders are invited to set right the machines if they are break down. The outsiders
come to the business office according to their convenience. No work is performed until
the machine is set right.
9.
Affect Urgent Work
The employees will be lazy after the mechanization of office work. The performance of
urgent work is affected during the period of break down of machines.
10.
Reduces Profit
There is no charging of depreciation before mechanization. After mechanization,
depreciation charges are high. This will reduce the profit.
11.
Obsolescence
Some machines may become obsolete within a short period.
12.
Slaves of Machines
Human beings may become slaves to the machines. Unless great care is taken, the
machines will become more important than the work it produces.
13.
Noise and Space Problems
The operation of machines may create noise. If adequate space is not available, it is very
difficult to use the machines.
14.
Dislocation of Work
A single person can be appointed to operate the machines. If he/she takes leave, there is a
dislocation of work. Thus, two operators are employed even though one would be enough.
3.2.4 Factors To Be Considered For Selecting Equipment
Following are some of the factor to be considered while selecting appropriate equipment:
(1) Ease of Operation: Faster operation, less fatigue, and fewer errors go with ease of
operations. Here are some contributory factors; indexing the amounts, operating the control
keys etc.
(2) Flexibility: Unless there is enough work to keep a highly specialized machine busy, it is
better to select one which can be used for different types of work. In absence of flexibility,
the purchase of the machine is not at all justified.
8
(3) Durability: A machine is used by different people under varying conditions. Unless, it is
strong and durable, it would be a poor investment.
(4) Portability: A machine is frequently moved from user to user or from one place to another
place in the same work area. Compactness and ease of handling saves time and energy and
Increase the use of the machine. Modern machine have been reduced in size and weight
without the sacrifice of the quality.
(5) Adaptability: If a machine can be used without disrupting an existing system, it would be
better to do so than go in for one which necessitates a considerable rearrangement of the
forms and records involved in extensive recopying of information and of adjustments in
procedures.
(6) Service: Reliable and continuous performance demands quick repairs and proper
maintenance. The machine which can be serviced promptly has advantage over one which
cannot be serviced.
(7) Operating cost: This includes such things as supplies, the space occupied, the special
equipment and forms required, repairs, etc.
(8) Reputation of the Supplier: Few people have the expertise to judge the mechanical
qualities of a machine so one has to depend upon the integrity of the manufacturer and dealer
to furnish a good machine and to backup claims and guarantees.
3.3 TYPES OF OFFICE MACHINE:
Various types of machines are available to perform the work smoothly. It is developed
for human for producing the human labor. Among all the machines, some of them are
described below:
1.
Computer:
Computer is an advanced electronic device. It is also modern device. Computer takes
any raw data from input unit and gives output as a result from output unit after the
processing unit. It does not have its brain so is depends on the user. Nowadays, computer
is the most useful device in office. We can multiply tasks from computer. We can collect
or store our important documents. Computer helps any kind of business. So it is one
useful type of machine.
9
Advantages of Computer:
1. Flexibility is possible since a number of programs can be prepared for different
business operations.
2. Provision of more information than otherwise possible.
3. Great accuracy and a total elimination of error possible.
4. Availability of control information at a great speed.
5. Better centralised managerial control is possible since a computer is usually installed
at the central office.
6. Indirect financial saving through various types of application inventory control is
possible.
7. Direct saving in office labor cost takes place.
8. Since monotonous manual office work is under taken by the computers, they reduce
the monotony of the staff.
9. Great speed with complicated calculations are possible only with the help of a
computer.
Disadvantages of Computer:
1. Computer Fraud: Though not very common, a computer fraud can be committed. If a
fraudulent inputs document is fed into the computer, or the system of computer, then the
fraud might take place. However, the fraud can be limited if a proper control system for
the computer is designed in consultation with the manufacturer.
2. Cost: Computers are very costly to install and run. This means that their usefulness
can be derived only by a large organisation.
3. Improper Assessment of Needs: It has been experienced in the West that an
organisation often underestimates their requirement for the computers. This results in an
increase in salary costs, and also inadequacy of equipment. The latter defect also leads to
more error and, consequently, more frustration and slowing of work.
4. Retrenchment: A single computer can take away the work performed by scores of
workers put together. Retrenchment of staff and consequent strained personal relations
are the direct result of computerisation in the office.
10
5. Centralisation of control: Use of the computer is centralised. Hence the control
mechanism also gets centralized in fact, it gets over-centralised. This results in the shift
in power to the computer room much to the disadvantage of the entire organisation.
6. Upsetting the Office System: To begin with, the computers upset all current office
systems and the routine of the business and may, therefore, initially adversely affect the
working in the office.
7. Technological Changes: A lot of time may elapse between the placing of orders for a
computer and its installation, which may range from 1 to 3 years. Since more and more
sophisticated models are manufactured, the ordered computer may be out of date to be
technically less competent.
8. Problem of Trained Staff: Properly trained staff for the computer is often short in
supply. However, the manufacturer can train internal staff for computer programming
and system analysis.
9. Cost of Breakdown: As and where a great amount of clerical works is done with the
computers, a breakdown may prove too costly. The office work will be completely
dislocated.
10. Costly Preparatory Work: Computers cannot be installed abruptly. Often preparatory
work for two to three years may be carried out which may prove to be quite costly.
2.
Typewriter:
Typewriter is the mechanical device replacing the role of work of writing letter by hand.
It is essential in all types of business organization. It increases the efficiency of letter
writing. It helps in writing letter neatly, cleanly and systematically.
This is a small but a pretty machine, needs no introduction at all because it is the heart-
throb of any office mechanisation. It has two commendable features of which the first is
for the neatness and clarity that it gives about the information, that it types and,
secondly, the number of copies that it can type says 6 or 7 including the original at a
stretch.
Types of Type-writer:
Type-writers come in different shapes and sizes. They also differ from each other on the
basis of their technical sophistication. Let us discuss the various types of type-writers
that a modern office can use.
11
Portable Type-writer:
These are light weighted, durable, sturdy and portable type-writers which are commonly
used by any individual. In our country the first such type-writer was marketed by the
stationery division of J.K. group. Later FACIT, REMINGTION, GODREJ, HALDA etc.
came into the picture to market this kind of type-writer.
Standard Size Type-writer:
Here the size of the type-writer is bigger as compared to the portable type-writer.
However, these are heavy as compared to portable type-writers, but their features are
same as the portable type-writer.
Multi-Lingual Type-writer:
India is a country which has so many states and union territories with different languages
and their scripts too are different. Hence the need of a system of type-writer wherein
different languages and their scripts could be typed. The need and desire of this system
of type-writers was felt. There are type-writers which not only has the Roman character
but Devanagri and characters of other alphabets etc.
Electric Type-writer:
Different studies in USA, Germany and India revealed that a busy typist hits about
50,000 characters in a day and his finger travels about 12 to 20 miles a day! To ease this
human effort, electric and electronic type-writers have been manufactured. Here the
work still has to be done by the fingers, but the physical effort involved in the process is
reduced considerably as the keys are just to be touched and need not be pressed.
An electrical type-writer has these advantages over the manual type-writer:
(a) It increases the speed of the work.
(b) There is a greater perfection in the work.
(c) The number of copies can be original plus 10 to 12 carbon copies instead of one plus
five of the manual system.
Special Purpose Type-writer:
There are special purpose type-writers which are used for typing mathematical and
scientific formulae and also for typing a special number of literatures. Different features
and different forms of parts are attached to these type-writers to type formats, master
12
sheets, mathematical and the scientific formulae.
Electronic Type-writer:
These were first manufactured in Japan by the companies like MINOLTA, OPTONICA,
MITSUBISHI—just to name a few. Over the years, certain Indian companies started
assembling these in India. The prominent of them were Gestetner, Modi, Pertech
Computer Limited, India Network Limited, etc. Certain features like right margin
alignment, left margin alignment, automatic erasure, tab set, bold type character,
automatic underlining, uses of italics character etc., and uses of various floppies of
characters make these types of type-writers unique machines to use in the office.
3.
Photocopy machine:
It is also known as 'xerox machine'. This machine is used to find out exact photographic
copy of original paper. The size of photocopy can be reduced and enlarged according to
the requirement.
Advantages of Photocopy:
1. Low Operating Cost: The operation cost of the photocopy is cheap.
2. Lower cost of labour: A copy can be taken out by pressing the button after the paper is
inserted. Hence this does not require any costly labor expense on training etc.
3. Versatility: It reproduces copies which may be difficult to reproduce in the ordinary
course.
4. Instant copies: Copies are obtained instantly.
Disadvantages of Photocopy:
In spite of holding a lot of advantages, photocopying has certain limitations and
drawbacks:
1. Shorter Life of The Copy: The life of the photocopy is short on account of two
reasons, the first is the paper used for photocopying is coated with chemical emulsion, as
a result of which it curls up instead of lying flat and this shortens the life of the copy.
2. Limited Number of Copies: This method is not suitable where, at a stretch, say 1,000
copies are to be taken out. In such circumstances, the duplicating machine suits better.
3. Uneconomical For a Large Number: Where copies are needed in large numbers,
13
photocopying may also prove a very expensive method. Instead, some of the duplicating
processes will be fast as well as economical. The cost of the copy with stencil duplicator
is very low.
4.
Calculator:
This is the most important component of the account department. This machine helps in
calculation with addition, deduction, multiplication, division, etc. For this purpose no
human mind is needed. If there is accuracy in instruction then calculation will be correct.
5.
Punching machine:
This is small and simple machine which is used to make small round holes in the left
edge of the papers. This is helpful to preserve the papers and documents for future
reference
6.
Scanner
While there is always a need to print things out, there might also be a need to convert a
printed document into a digital form. That is where scanners come in. They can take
anything, be it a letter, an image, a photo film or even a face, and make it digital.
Scanners come in handy when you need to digitize some old documents or scan a
physical photograph of a new employee. Additionally, you can even transform the
scanned documents back into text form with the use of additional software.
7.
Shredders
Every company has confidential materials that should never end up in the wrong hands.
This includes personal files on past and present employees, secret files or financial
documentation. If there were a need to dispose of them, it would be inappropriate to
simply throw them in the trash, as someone might find them and use them to their
advantage. That is why most offices need shredders. They come in all sizes: some are as
small as shoeboxes, while others are as large as closets. The size of a shredder should
depend on the size of the company and the amount of documents that might need to be
destroyed.
8.
Telephone:
Telephone is a system for talking to somebody else over distance using wires or radio. It
is one of important and modern means of communication. It brings quick transformation
14
of information through the personal talks. Different types of secret works are done
through the help of telephone.
10. Fax
Fax (short for facsimile), sometimes called telecopying or telefax (the latter short for
telefacsimile), is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material (both text and
images), normally to a telephone number connected to a printer or other output device.
11. Laminating Machines
Laminating machines are generally underutilized in most offices. When someone has
gone to the trouble to print or copy a document, that document can be preserved by heat-
sealing two thin layers of clear plastic over each side.
12. Label Makers
Like a laminating machine, a label maker might seem more like an extra than a needed
piece of office equipment, but if this is the case, then it may be that one simply does not
realize the scope of what can be done with such a handy gadget.
13. Printer
A printer is any device that prints text or illustrations on paper. A printer is a peripheral
which makes a persistent human-readable representation of graphics or text on paper or
similar physical media. There are many different types of printers.
Based on Technology
Daisy-Wheel: Similar to a ball-head typewriter, this type of printer has a plastic or metal
wheel on which the shape of each character stands out in relief. A hammer presses the wheel
against a ribbon, which in turn makes an ink stain in the shape of the character on the
paper. Daisy-wheel printers produce letter-quality print but cannot print graphics.
Dot-Matrix: Creates characters by striking pins against an ink ribbon. Each pin makes a
dot, and combinations of dots form characters and illustrations.
Ink-Jet: Sprays ink at a sheet of paper. Ink-jet printers produce high-quality text and
graphics.
Laser: Uses the same technology as copy machines. Laser printers produce very high
quality text and graphics.
15
Line Printer: Contains a chain of characters or pins that print an entire line at one time.
Line printers are very fast, but produce low-quality print.
Printer Characteristics
Printers are also classified by the following characteristics:
Quality of type: The output produced by printers is said to be either letter quality (as
good as a typewriter), near letter quality, or draft quality. Only daisy- wheel, ink-jet, and
laser printers produce letter-quality type.
Speed: Measured in characters per second (cps) or pages per minute (ppm), the speed of
printers varies widely. Daisy-wheel printers tend to be the slowest, printing about 30 cps.
Line printers are fastest (up to 3,000 lines per minute). Dot- matrix printers can print up to
500 cps, and laser printers range from about 4 to 20 text pages per minute.
Impact or non-impact: Impact printers include all printers that work by striking an ink
ribbon. Daisy-wheel, dot-matrix, and line printers are impact printers. Non- impact printers
include laser printers and ink-jet printers. The important difference between impact and non-
impact printers is that impact printers are much noisier.
Graphics:Some printers (daisy-wheel and line printers) can print only text. Other printers
can print both text and graphics.
Fonts : Some printers, notably dot-matrix printers, are limited to one or a few fonts. In
contrast, laser and ink-jet printers are capable of printing an almost unlimited variety of
fonts.
14. Stenographic machines
The common practice is that shorthand typist takes dictation in his note-book and
transcribes it in letters. The officer sits along with his stenographer and dictates the letters;
the latter after taking them down types in letter pads, making the letters ready for
signature.The new invention of dictation machines has come into use. These types of
machines make it possible for the officers to dictate letters at their convenience. Then the
recorded tape is sent to the typist, who fixes the recorded tape on a reproducing machine
and types it by hearing the recorded dictation. The speed of the playback can be adjusted
to the speed of the typist through controls.There are many methods of making outward
correspondence ready. They are (a) giving dictation to a stenographer (b) dictating directly
to a typist, who types out at the same time (c) dictation to a stenographic machine (d)
16
recording a dictation in a dictation machine.Dictating machines have become very popular
nowadays. Replies to correspondence can be made through the machines. The officer gives
the dictation through a mouthpiece, which is connected to the machine, and the message is
impressed, on a disc. The disc is placed on another machine; and through an earphone the
dictated portion is reproduced; and the typist types out the letter. The dictated message can
be erased and the disc can be reused. The speed can also be regulated according to the speed
of the typist.
The stenographic machine is portable and noiseless. The keyboard on the machine is
pressed down by the stenographer, when a word is heard. The machine is operated at a good
speed by a trained operator. The tapes are passed on to the typist, who is trained to read and
type from these tapes. This machine is very useful for recording at meetings, reporting, etc
Merits of Stenographic Machine
1. The executive can dictate or give reply even if the stenographer is absent.
2. The number of clerks can be reduced.
3. Salary to stenographers is paid high and salary to typist is low. Instead of appointing
stenographers, typists can be appointed. It is more economical.
4. All stenographers may not be able to take dictation at a high speed. If the stenographic
machine is available, the executive can dictate the reply at any speed. When the typist
types, the speed of the tape or disc can be regulated.
5. It is usual that visitors may come often and often during the dictation and waste the time
of the stenographer. Such waste of time can be avoided.
Demerits of Stenographic Machine
1. Personal contact is neglected.
2. It is very difficult to make correction in Dictaphone.
3. Since tape or disc is used again and again, original records cannot be maintained.
4. For efficient operation of the machine, the executive must be a good dictator.
Questions
PART A
1. Distinguish between office automation and office Mechanisation.
2. Explain Paperless office.
3. Define the term Automation.
4. State the objectives of Automation.
17
5. Write short notes on: a) Laptop b) Pen drive.
6. State the importance and use of paper shredder.
7. List out the types of Printers.
8. Analyze the role of machine in modern office.
9. Examine the advantages and disadvantages of using personal computers in office.
10. Outline the significance of photocopier machines in an office.
PART B
1. Describe, the various types of copying machines used in modern office.
2. Discuss the Objectives of Office Mechanisation.
3. Summarize the advantages and disadvantages of Mechanisation in an office
4. Determine the factors to be considered for selecting equipment.
5. Describe few modern machines used in an office to ensure work is performed
smoothly.
6. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of stenographic machine in an office
References
1. Office Management By Prasanta K. Gosh
2. Office Management By Katherasan and Dr.Radha
3. Office Management and Secretarial Practice By . I.M.Sahai,

1
SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
UNIT – IV - OFFICE MANAGEMENT– SBAA1407
2
IV. BANKING FACILITIES AND MODE OF PAYMENTS
4.1 BANKING FACILITIES
A bank is a financial institution that provides banking and other financial services to their
customers. A bank is an institution which provides fundamental banking services such as
accepting deposits and providing loans. Banks are a subset of the financial services industry.
A bank is an organisation whose principal operations are concerned with the accumulation of
the temporarily idle money of the general public for the purpose of advancing to others for
expenditure.”-R.P. Kent
“Banking is the business of accepting for the purpose of lending or investment, of deposits of
money from the public repayable on demand or otherwise and withdraw-able by cheque,
draft, and order or otherwise.” Indian Banking Regulation Act, 1949
4.1.1 IMPORTANCE OF BANK FOR BUSINESS
1. Collections of Savings and Advancing Loans
Acceptance of deposit and advancing the loans is the basic function of commercial banks. On
this function, all other functions depend accordingly. Bank operates different types of
accounts for its customers.
2. Money Transfer
Banks have facilitated the making of payments from one place or persons to another by
means of cheques, bill of exchange and drafts, instead of cash. Payment through cheques, the
draft is more safe and convenient, especially in case of huge payments, this facility is a great
help for traders and businessmen. It really enhances the importance of banks for the business
community.
3. Encourages Savings
Banks perform an invaluable service by encouraging savings among the people. They induce
them to save for profitable investment for themselves and for the national interest. These
savings help in capital formation.
4. Transfer Savings into Investment
Bank transfer the savings collected from the people into investment and thus increase the
amount of effective capital, which helps the process of economic growth.
3
5. Overdraft Facilities
The banks allow the overdraft facilities to their trusted customers and thus help them in
overcoming temporary financial difficulties.
6. Discounting Bill of Exchange
The importance of banks can be seen through the facility of discounting the bill of exchange.
Banks discount their bill of exchange of consumers and help them in financial difficulties. By
discounting a bill of exchange, they able to get the desired amount for the investment they
want.
7. Financing Internal & External Trade
Banks help merchants and traders in financing internal and external trade by discounting a
foreign bill of exchange, issuing of letters of credit and other guarantees for their customers.
8. Act as an Agent
The bank act as an agent and help their customers in the purchase and sales of shares,
provision of lockers payment of monthly and dividends on the stock.
9. Issue of Traveler‟s Cheques
For the convenience and security of money for travelers and tourists, the bank provides the
facility of traveler‟s cheques. These cheques enable travelers and tourists to meet their
expenses during their journey, as these are accepted by issuing bankers, restaurants, and other
businessmen both at home and abroad. No doubt, this is also one of the great functions of
banks and shows the importance of banks for us in more precise ways.
10. General Utility Services
The existence of commercial banks is essential for contribution to general prosperity. Banks
are the main factors in raising the level of economic development of the world. In addition to
the above-cited advantages, banks also provide many services of general utilities to the
customers and the general public.
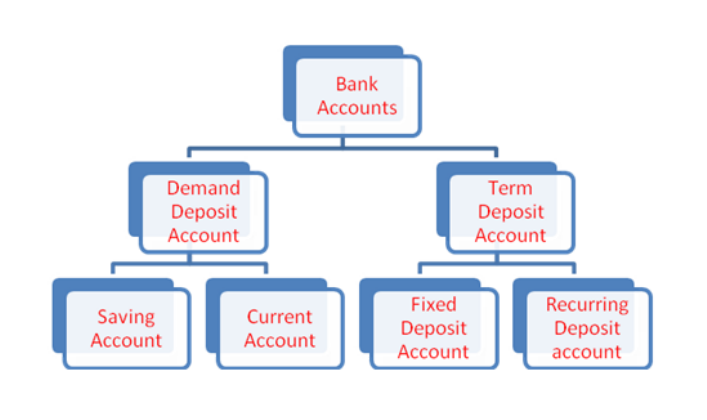
4
4.1.3 TYPES OF ACCOUNTS
Demand deposit accounts allow funds to be withdrawn at any time from the financial
institution. Demand Deposits accounts are Current accounts and Savings accounts
Time deposit is a bank deposit that has a fixed term and interest rate. The funds in this
account cannot be withdrawn for a specific term. Recurring Deposits accounts and Fixed
Deposit accounts are Time Deposit accounts.
Current Account
These are payable to the customer whenever they are demanded. When a banker accepts a
demand deposit, he incurs the obligation of paying all cheques etc. drawn against him to the
extent of the balance in the account. Because of their nature, these deposits are treated as
current liabilities by the banks. Bankers do not allow any profit on these deposits, and
customers are required to maintain a minimum balance, failing which incidental charges are
deducted from such accounts.
• Withdrawal is made through cheques
• No restrictions on withdrawal
• No interest is given
• Generally opened by businessmen
• Overdraft facility
5
Overdrafts Facility:
• A bank may extend credit up to a maximum amount (called overdraft limit) against a
current account. Customer can write checks or make withdrawals from his account.
• The most common form of business borrowing, is an overdraft. It is a type of
revolving loan where in funds are available as to when required. Interest is charged only
on the daily overdraft (debit) balance.
• Such loans area demand loans. The facility can be cancelled (and entire outstanding
amount „called‟) at any time by the lender at its discretion, without any warning notice
or explanation.
• If the overdraft is secured by an asset or property, the lender has the right to foreclose
on the collateral in case the account holder does not payor the borrower‟s credit rating
falls or the lender has reason to believe the borrower may go into default.
• An overdraft is approved only for a fixed period (usually one year) after which it must
be renegotiated.
Savings Account
The main object of the savings deposits is to encourage thrift among people who can deposit
only a very small amount at a time.
• Withdrawal is made through cheques.
• Restrictions on withdrawal of money i.e. the account holder can‟t make more than 8
withdrawals in a month.
• Small amount of interest is given.
• Generally opened by small savers
• No overdraft facility is given
Fixed account:
The deposits that can be withdrawn after a specified period of time are referred to as Fixed or
Term Deposits. The period for which the bank keeps these deposits ordinary varies from
three months to five years in accordance with the agreement made between the customer and
the banker. Interest/ return is paid to the depositors on all Fixed or Time Deposits, and the
rate of interest/ return varies with the duration for which the amount is kept with the banker.
Many depositors keep their money in Fixed Deposits with banks as investment because of the
interest/return paid on them. Since fixed or term deposits remain with the bank for a specific
6
period, they can be profitably employed. By lending out or investing these funds, the bank
earns more than the interest/return that it has to pay on them to the depositors.
No use of cheques.
Withdrawal is not allowed before maturity
High rate of interest is given.
No overdraft facility is given
Advantages of Fixed Deposits
100% safe as all the banks operating in the country
All bank deposits are insured under the Deposit Insurance Scheme up to a colum of
Rs1,00,000 per a/c
One can get loans up to 75- 90% of the deposit amount from banks against fixed
deposit receipt
Tax deduction under section 80C but interest is taxable, if interest more than
10,000 , TDS will be applicable.
Recurring Deposit
Under Recurring deposits are Fixed amounts are deposited at regular intervals for a fixed
term and the repayment of principal and accumulated interest is made at the end of the term.
These deposits are usually targeted at persons who are salaried or receive other regular
income. A Recurring Deposit can usually be opened for any period from 6 months to 120
months. Any default in payment within the month attracts a small penalty.
Features of Recurring Deposits:
• Fixed amount is deposited at regular intervals for a fixed term and the repayment of
principal and accumulated interest is made at the end of the term.
• A customer can prematurely withdraw his Term Deposit. However, Bank will charge a
penal interest of 1% on the amount so withdrawn.
• The rate of interest on such deposits keeps on varying with market rates.
Advantages of Recurring Deposits:
• Compulsion to save
• High rates of interest as compared to Term Deposits
• Liquidity to access those savings anytime
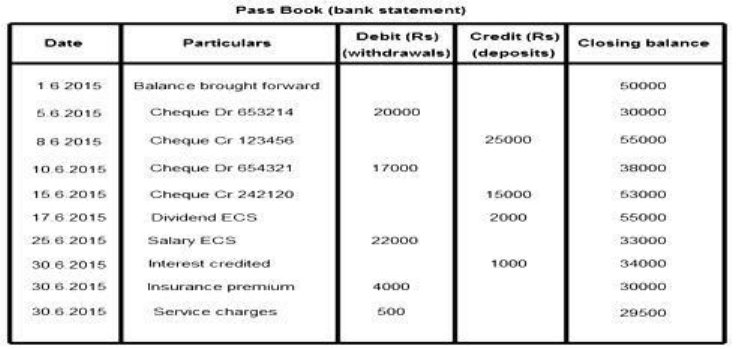
7
4.2 BANK PASS BOOK AND CHEQUE BOOK
Bank passbook is a book that records the bank transactions in a savings account. It is the
exact copy of the customer‟s account in the bank‟s book. It records the deposits, withdrawals,
interest credited, bank charges, etc. during a financial year. The passbook is issued by the
bank to its customers. The customer has to retain it and periodically update it to enter recent
transactions. With the help of Passbook, a customer can keep an eye on the entries made in
his account by the bank. As and when the entries are updated in the passbook the customer
can check them and inform the bank, if he finds any error regarding the entries made.
Specimen of a Pass book
Cheque Book
Cheque is a very popular negotiable instrument. If you have a savings bank account or
current account in a bank, you can issue a cheque in your own name or in favour of others,
thereby directing the bank to pay the specified amount to the person named in the cheque. A
cheque is an order by the account holder of the bank directing his banker to pay on demand,
the specified amount, to or to the order of the person named therein or to the bearer.
Advantages
It is one of the safest and convenient modes of making payments and is transferred by
mere delivery.
One of the benefits of the cheque is that you can transfer a high-value transaction
without any hassle which would be very difficult if hard cash was used instead.
The issuer of the cheque has an account (savings or current) with the bank to which it
is connected.
8
Some of the important details which should be present in a cheque are as follows
A cheque should be dated.
A cheque should mention the amount of money in figures and words.
A cheque must be signed by the person (Drawer) issuing the cheque
A cheque must be drawn upon a specified bank (Drawee).
A cheque must have the name of the recipient (Payee) of the cheque
4.3 TYPES OF BANK DOCUMENTS
1. Deposit slip: A deposit slip or challan is a form supplied by a bank for a depositor to
deposit money in the bank. It is a blank form provided by the bank to facilitate account
holders to to deposit cash or cheques in the account. Since authorization is not required for
depositing money, anybody can deposit money to any account.
2. Withdrawal slip: A Withdrawal Slip is a written order to your bank instructing it to
withdraw funds from the account. Withdrawal slips vary from bank to bank .A customer
can withdraw cash using withdrawal slip only at their home branch.

9
3. Demand Draft : Demand Drafts is a pre-paid instrument, wherein bank by whom the
DD has been made undertakes responsibility to make full payment. DD is valid for 6
months. Demand draft is accepted where the transfer of money is guaranteed.
4. Cheque: It is the most preferred mode of withdrawing cash from the bank account. Instead
of using it for withdrawing cash it is majorly used for making payments. The cheque is a
negotiable instrument containing an order to a bank to pay a stated sum from the drawer‟s
account, written on a specially printed form. It is signed by the drawer. It can be easily
transferred through a mere hand delivery. There are three parties to the cheque-Drawer
(maker of the cheque), Drawee (bank on which the cheque is drawn), Payee (to whom the
amount of the cheque is payable).
10
Table Showing Difference between Cheque and Demand Draft
Basis For
Comparison
Cheque
Demand Draft
Order of
payment
By the account holder to
the bank.
By the branch of a bank to
another branch of the same
bank.
Payment
Payable either to order or
to bearer.
Always payable on demand to a
specified party.
Issuance
The cheque is issued by a
customer of the bank.
Demand Draft is issued by a
bank.
Bank Charges
for issuance
No
Yes
Drawer
Customer of the bank.
Bank itself.
Signature
It must be signed by the
party issuing it, be it an
individual or authorized
signatory of a firm.
It contains seal and signature of
the authorized officer and the
rubber stamp of the bank.
Parties Involved
Three Parties
Two Parties
Dishonor
Yes
No
Parties to a Cheque:
a. The drawer: The person who draws the cheque.
b. The drawee: The banker of the drawer on whom the cheque is drawn.
c. The payee: one to whom the sum stated in the cheque is payable, either the drawer
himself or any other person may be the payee.
d. The holder: is either the original payee or any other person to whom, the payee has
endorsed the cheque. In case of a bearer cheque, the bearer is the holder.
e. The endorser: when the holder endorses the cheque to anyone else, the latter
becomes the endorser.
f. The endorsee: is the person to whom the cheque is endorsed.
11
Essentials of a Cheque
It is always drawn on a banker where the drawer has an account.
It is always payable on demand.
It does not require acceptance. There is, however, a custom among banks tomark
cheques as good for purposes of payment.
Cheques may be payable to the drawer himself. It may be made payable to bearer
on demand unlike a bill or a promissory note.
The banker is liable only to the drawer. A holder has no remedy against the banker
if a cheque is dishonoured.
A cheque is usually valid for 3months in India. However, it is not invalid if it is
post dated or antedated.
No Stamp is required to be affixed on cheques.
4. Bank advice: A bank may provide a couple of additional services like collecting and
paying periodic amounts on behalf of the bank account holder as per the standing
instructions given by the account holder. An intimation of such collection and payment
sent by the bank to account holder is known as bank advice.
Other Forms
Money transfer forms -When you need to transfer money from your account to
someone else
Loan application forms – When you file for the loan.
Other Online forms for Banks
o Bank Account Information Form
o Bank Accounts Opening Form
o Bank Account Registration Form
o Bank Authorization Form
o Bank customer Feedback Form
o Bank Information Form
o Bank Rating Form
12
o Bank Reference Form
o Bank Verification Form
o Credit Card Application Form
o Internet Banking Form
o Loan Application Form
o Mobile Banking Survey Form
o Bank Loan Estimate Form
o Small Business Credit Application Form etc.
4.4 ATM & MONEY TRANSFER
4.4.1 ATM (Automated Teller Machine )
An automated teller machine (ATM) is an electronic banking outlet that allows customers to
complete basic transactions without the aid of a branch representative or teller everyday
banking like deposits and withdrawals. Although the design of each ATM may be different,
they all contain the same basic parts:
Card reader: This part reads the chip on the front of the card or the magnetic stripe on the
back of the card.
Keypad: The keypad allows the consumer to input information like the PIN, the type of
transaction he or she intends to do, and the amount of the transaction.
Cash dispenser: Bills are dispensed through a slot in the machine, which is connected to a
safe at the bottom of the machine.
Printer: If required, consumers can request receipts that are printed here. The receipt
records the type of transaction, the amount, and the account balance.
Screen: The ATM issues prompts that guide the consumer through the process of
executing the transaction. Information is also transmitted on the screen, such as account
information and balances.
Transactions in ATM
1. Deposits,
2. Withdrawals,
13
3. Fund transfers, and
4. Balance Enquiry and mini statements.
Advantages
1. Provide Convenience to Customers
Customers are able to do financial transactions conveniently with the use of ATMs. They
can avail various banking services and can do payments seating at their home comfort.
Various payments for online shopping, at restaurants and various other places payment can
be made using ATM. Nowadays ATM are installed at all important places like railway
station, airports, hospitals etc. which facilitate the people in withdrawing their money
whenever they want.
2. Offer 24×7 Service
ATMs provides 24 hours a day, 7 days a week and 365 days a year to all its customers.
Unlike bank branches, it does not have any time schedule for its operations. Customers
can access their bank accounts and withdraw their money at any time of day or night as
per their convenience.
3. Reduce Banks Workload
ATMs have an efficient role in reducing the workload of the banking industry. It has
relieved customers as they can avail various banking services by using ATM without
visiting the bank branches. Customers are not required to stand in long queues and fill up
various forms for availing basic withdrawal and deposit facilities. It helps in reducing the
work pressure on bank staff and provides flexibility to its operations.
4. Access to Bank Account from Anywhere
Account can be accessed by customer using ATM from any part of the country or even
worldwide. ATM machines are installed in different parts of the country at all convenient
places. Customers don‟t need to carry cash while travelling and they can easily withdraw
money any place they are travelling.
5. Minimizes Transactions Cost
ATM has reduced the manpower need as all transactions are processed and monitored
using automated computerized systems. There is less human intervention in work
operations which reduce overall cost.
14
Disadvantages of ATM
1. Charges Fees
Usage of ATMs by customers invites charging various fees for using it. Bank charges
routines charges as per their standard rates for providing them ATM facility. Customers
are also required to pay various tax while doing transactions online using the ATM.
Limitation On Cash Withdrawal
Bank imposes restrictions on withdrawal limit of their customers using ATM. There are
limitations on both no. of free transactions and the amount of money that can be
withdrawn per transactions. Banks set withdrawal amount limit for their customers. Most
of the banks do not allow withdrawal of more than 25,000 at a time.
2. Possibility Of Frauds
Customers performing online transactions using ATM are likely to be affected by various
frauds. There is a chance of stealing various account information by online hackers while
doing online transactions. These online hackers through various suspicious activities can
get access to your account and loot your money.
3. Non-Reachable In Rural Areas
Banks in rural areas of our country have limited computerized branches and depends
mainly on manpower for its various operations. There are limited ATM machines installed
in rural areas which also do not operate properly. Therefore ATM services are not properly
available in rural areas.
4.4.2 MONEY TRANSFER
There are numerous ways of transferring money from one bank account to account. With the
increasing technology, online money transfer has become the easiest way of transferring only
from one bank to another without any difficulty. Here are three major means of transferring
money.
1.
NEFT (National Electronic Fund Transfer)
NEFT is a system similar to RTGS with certain differences. RTGS handles big ticket
transactions, whereas NEFT handles smaller size transactions. Most branches are using this
facility to transfer funds in an efficient manner. Once the applicant for the transfer of funds
furnishes full and correct details (correct account details means correct name of the
15
beneficiary, the correct account number, the branch and bank of the beneficiary, and the
correct IFS code, etc.) funds can be transferred to the beneficiary„s account by the remitting
bank. Transfer of funds through NEFT is safe, quick. It reduces the paper work and is cost
effective.NEFT is an innovative electronic media for effecting transfer of funds. Special
features of NEFT are:
NEFT is a funds transfer system which enables a customer of a bank to transfer
fundsto another customer of another bank having account with any participating
bank
NEFT allows both intra and inter-bank funds transfer within a city and across
cities. Since it is in the form of e transfer, without any physical movement of
instruments, funds can be transferred quickly
The beneficiary customer gets funds in his account on the same day or at the
earliest on the next day depending upon the time of settlement
Both the originating and destination bank branches should be on NEFT platform
The correct details of IFSC, beneficiary„s name, account numbers, etc., should be
furnished to the originating bank.
The originating bank branch can keep track of the status of the NEFT transaction.
In case for any reason the destination branch is not able to afford credit to the
beneficiary„s account, destination branch/bank have to return the funds to the
originating bank within two hours of completion of the batch through which the
transaction was processed
It is not only easy method of transfer of funds, but also enables the remitters to
have user friendly and cost effective transfer of funds.
2.
RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement )
One of the important IT revolutions in Indian Banking Scenario was the implementation of
the Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) system by the Reserve Bank of India. With the
changing scenario from manual environment to electronic mode, banks started to use faster,
safer and efficient methods to transfer funds. In this regard, two important and popular
electronic funds transfer systems are Real Time Gross System (RTGS) and National
Electronic Funds Transfer System (NEFT) RTGS is an electronic payment system, where
16
payment instructions are processed on a ‗continuous„ or ‗REALTIME„ basis and settled on
a ‗GROSS„ or ‗individual„ basis without netting the debits against credits. In India, RBI
introduced this system and the system is functioning well. The payments so effected are
final„ and irrevocable„. The settlement is done in the books of the central bank (RBI). The
RTGS system allows transfer of funds across banks on a real time (immediate) basis. Each
participant bank needs to open a dedicated settlement account for putting through its RTGS
transactions. Not only does it allow transfer of funds, it also reduces the credit risk. Both
customers and banks can transfer funds monies the same day at regular intervals within the
banking hours
(a) Real Time Gross Settlement helps banks to settle interbank and forex settlements
(b) It also helps banks in handling big ticket funds transfers
(c) Since RTGS it is routed through RBI platform, the credit risk is minimized
(d) Unlike in case of cheque clearance, the drawer of the cheque cannot enjoy the float time
(the date of issuance of cheque and the date on which it is received in inward clearing and
debited by his banker) However, in the case of RTGS, the remitter„s account is debited first
and then only the funds are transferred
(e) If all relevant details such as the beneficiary„s name, account number, IFSC code of the
receiving branch, name of the beneficiary bank, etc., are correctly furnished it would assist
the remitting bank to effect the transfer quickly
(f) As the name RTGS suggests, the transfer mechanism works on real time and, therefore,
the beneficiary branch/bank should receive the funds immediately. The beneficiary„s
branch/bank should give credit to the beneficiary„s account immediately or latest within 2
hours of receiving the funds transfer message. However, in case the funds cannot be credited
for any reason, such funds should be returned to the originating branch within two hours. In
such a situation, as soon as the money is returned, the remitting bank should reverse the
original debit entry in the client„s (remitter„s) account. This system is applicable between
banks/branches who are on Core Banking Solutions (CBS)
3.
IMPS (Immediate Payment Service)
IMPS stands for Immediate Payment Service in Indian banking system terminologies. It is a
money transfer mechanism made available by the apex bank of the country, the Reserve
Bank of India and the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI). Initiated in 2010 by
17
the NPCI with the help of a pilot project with 4 major banks, IMPS has now grown to 150+
banks. The major feature of IMPS is that it is available at all times for usage. It transfers
funds instantly and is a great banking platform in case of emergencies. The transaction
charges of this platform are also very nominal and the transfer limit is also considerable,
approximately Rupees 2 lakhs per day. Moreover, IMPS is available on mobile too which
makes it super-convenient. National Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT) and RTGS (Real-time
gross settlement) transfer mechanisms are only available during their business hours.
Moreover, NEFT and RTGS are not available on bank off-days and holidays. However,
IMPS scores a point in this regard as it is available 24 x 7.National Payments Corporation of
India (NPCI) is responsible for managing the IMPS fund transfer mechanism. This
mechanism is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India. One can define IMPS as an
immediate, inter-bank real-time fund transfer mechanism enabled through electronic means.
4.
UPI (Unified Payments Interface):
A Unified Payment Interface (UPI) is a smartphone application that allows users to transfer
money between bank accounts. It is a single-window mobile payment system developed by
the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI). It eliminates the need to enter bank
details or other sensitive information each time a customer initiates a transaction. The
Unified Payment Interface is a real-time payment system. It is designed to enable peer-to-
peer inter-bank transfers through a single two-click factor authentication process. The
interface is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), India's central bank. It works by
transferring money between two bank accounts along with a mobile platform.
The system is said to be a safe and secure method of transferring money between two parties
and eliminates the need to transact with physical cash or through a bank. The pilot system
was launched in India on April 11, 2016. Banks across the country started to upload their
interface in August 2016.
A Unified Payment Interface (UPI) is a smartphone application for banking in India.
The interface is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), India's central bank,
and funds sent between accounts.
This app eliminates the need to enter bank details or other sensitive information each
time a customer initiates a transaction making it a safe way to bank.

18
4.5 TYPES OF PAYMENTS HANDLED
Payment Systems can be broadly classified into Large Value Systems and Retail Payment
Systems. For the purpose of making things easy to understand we have classified the various
payment methods in the following format:
1. Large Value Payment System:
These options are used by individuals or businesses to perform large value payments, and
usually the money transfer across in a delayed fashion. Delayed here implies, that the
settlement between the accounts/banks happen in at defined settlement timings. Large value
payments are facilitated through RTGS, NEFT , ECS & Cheque
2. Retail Payment System:
i. Cash Payment
ii. Cheques
iii. Demand Drafts
iv. Card-Based Payments
Credit Card
Debit Card
v. Electronic Payments and Remittances
Electronic Clearing Services:
Electronic Funds Transfer:
Real-Time Gross Settlement:
Internet Banking:
Mobile Banking
Digital Wallets
i. Cash – is the preferred method for small payments because it involves no credit and
therefore no promises. With cash, you can usually purchase goods and services easily as it
widely accepted. Carrying too much cash is risky as it can lead to theft and other problems.
However, people still carry cash for its convenience and flexibility. From the payee‟s point
of view, transactions are completed immediately and this cash can be re-used for other
transactions.
ii. Cheques – a cheque is an order to transfer funds from the payer‟s bank to the account of
the payee. Cheques are generally valid for six months after the date of issue. The use of

19
cheques has traditionally dominated Fijian non cash payments. Despite the development of
other payment instruments, cheques remain an important form of payment. A cheque is
effectively a future promise to pay the amount stated on it and needs to be presented to a
bank in order to obtain the payment. Cheque clearance usually takes 3 - 4 working days.
Advantages
Safer than cash e.g. a crossed cheque can only be deposited into the payee‟s account.
Preferable for large amounts and a large number of payments to avoid carrying large
sums of cash.
Payments can be made at your convenience and posted to the payee.
Disadvantages
Can take up to 3 – 4 working days before funds are available to use.
There is no guarantee that the payer has sufficient funds and hence the cheque may
become dishonored (bounce) by the bank.
There are extra costs if the payee wants an immediate clearance of funds. Cheques
also have other administrative costs associated to it.
iii. Demand Drafts
A demand draft or a DD is a negotiable instrument issued by the bank. The bank issues the
draft to a client (drawer) directing another bank or own branch to pay the specific amount to
the payee. The drafts are payable on demand. It cannot be paid to the bearer but the
beneficiary has to present the instrument directly to the branch. It can also be collected by
the clearing mechanism of the bank.Mostly, demand drafts are issued in situations where
the parties are unknown to each other and lack trust. It comes handy in such situations as
there are almost no chances of fraud and counterfeiting
iv. Card-Based Payments
Debit Card – is a payment card where the transaction amount is deducted directly from the
card holder‟s bank account upon authorization.
Advantages
Card payments will only be accepted if the card holder has sufficient funds in his/her
account.

20
Can be used for mail order or online purchases.
Less risk than holding cash. The risk of theft is mitigated by having pin codes.
Disadvantages
Takes up to three days for money to be received and acknowledged.
Operated at a fee payable to the bank.
Credit Card – enables its holder to buy goods and services with a credit line given by
credit card issuer. Funds are settled at a later date. Card holders are billed on a monthly
basis and bear financial charges (interest) on outstanding amounts if payments are not made
by the due date. Credit cards are issued through commercial banks and/or other issuers.
Advantages
Guaranteed payment up to an approved limit.
Can be used for mail order and online purchases.
Disadvantages
A fee is paid to the bank for this service.
High interest rates make credit cards an expensive mode of borrowing.
Theft – if the card is stolen or if internet payment sites are not secure.
V. Electronic Payments and Remittances
Electronic Clearing Services
ECS is an electronic mode of funds transfer from one bank account to another. It can be
used by institutions for making payments such as distribution of dividend interest, salary,
pension, among others. It can also be used to pay bills and other charges such as telephone,
electricity, water or for making equated monthly installments payments on loans as well as
SIP investments.
Payee needs to inform the bank and provide a mandate that authorises the institution, who
can then debit or credit the payments through the bank. The mandate contains details of
your bank branch and account particulars. It is the responsibility of the institution to
communicate the details of the amount being credited or debited to their account, indicating
the date of credit and other relative particulars of the payment. The ECS user can set the
21
maximum amount one can debit from the account, specify the purpose of debit, as well as
set a validity period for every mandate given.
Advantages
Increases customer satisfaction
No late payment fees
Makes prompt payments of bills
Enables customers to make timely payment of insurance premiums, credit card
payments, mobile and telephone bills, mutual funds, loan instalments, etc.
Reduces the use of papers
NEFT (National Electronic Fund Transfer)
The National Electronic Fund Transfer or NEFT is the simplest and most liked form of
money transfer from one bank to bank. To make any NEFT transaction, you just need two
important pieces of information -- firstly, account number and secondly, the IFSC Code of
the destination account. In NEFT, there is no cap on the amount of money that can be
transferred. However, individual banks may set a limit.
RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement )
A Real Time Gross Settlement or RTGS is almost similar to NEFT but the minimum
payment and how it credits to the destination account differs. If you want to transfer more
than 2 then you can use this. There is no upper cap on the amount. An RTGS money
transfer happens on a real-time basis. The bank of the person to whom the money is
transferred gets 30 minutes to credit it to his/her account.
Internet Banking – a fast and convenient way of performing banking transactions such as
transferring funds from your savings to current account or to a third party account.
Advantages
Payments are made at your convenience.
Secured by user name and password.
Can be used from anywhere in the world with internet access.
Disadvantages
Access to computers and internet services is required.
22
Internet comes at an additional cost.
Mobile Banking - a service provided through the combined effort of a bank and a mobile
service provider, to perform common banking transactions. An active bank account is
needed and a mobile phone equipped with features required by the bank.
Advantages
Secured to ensure user information is available anytime.
Fast and convenient.
Payments may be made from anywhere that has your mobile network coverage.
Disadvantages
Mobiles need to be kept safely, otherwise misuse may occur.
Mobile phones come at a cost and need to be recharged.
Mobile Money/ Digital Wallets
Digital wallets allow customers to make payments to selected merchants and other
individuals through their mobile phones. Bill payments and purchases of goods and services
are among the cashless transactions that can be made. To enjoy the benefits of mobile
money, the customer has to register and open an account with the mobile money service
provider.
Advantages
Fast, reliable and efficient mobile payments may be made at any time of the day.
Convenient for making payments to and receiving payments from people in remote
areas.
Available in any part of the country where there is network coverage.
The mobile wallet is protected by a pin and if the phone is lost/stolen your money is
safe.
23
4.6 TYPES OF CHEQUE
Open cheque, and Crossed cheque.
Bearer cheque andOrder cheque
Ante-dated cheuqe , Post-dated cheque and Stale Cheque
Mutilated Cheque
Open cheque: A cheque is called „Open‟when it is not crossed and can be encashed over
the counter at the bank. The holder of an open cheque can do the following:
Receive its payment over the counter at the bank,
Deposit the cheque in his own account
Pass it to someone else by signing on the back of a cheque.
Crossed cheque: Since open cheque is subject to risk of theft, it is risky to issue such
cheques. This risk can be avoided by issuing another types of cheque called „Crossed
cheque‟. The payment of such cheque is not made over the counter at the bank. It is only
credited to the bank account of the payee. A cheque can be crossed by drawing two
transverse parallel lines across the cheque, with or without the writing „Account payee‟ or
„Not Negotiable‟.
Bearer cheque: A cheque which is payable to any person who presents it for payment at the
bank counter is called „Bearer cheque‟. A bearer cheque can be transferred by mere delivery
and requires no endorsement.
Order cheque: An order cheque is one which is payable to a particular person. In such a
cheque the word „bearer‟ may be cut out or cancelled and the word „order‟ may be written.
The payee can transfer an order cheque to someone else by signing his or her name on its
back.
Ante-dated cheques: Cheque in which the drawer mentions the date earlier to the date of
presenting if for payment. For example, a cheque issued on 20thMay 2015 may bear a date
5thMay 2015.
Post-dated Cheque: Cheque on which drawer mentions a date which is subsequent to the
date on which it is presented, is called post-dated cheque. For example, if a cheque
presented on 8
th
May 2015 bears a date of 25thMay2015, it is a post-dated cheque. The bank
will make payment only on or after 25thMay 2015.
24
Stale Cheque : A cheque becomes stale after lapse of three months from the date of the
cheque if it is not presented for payment by the payee or the holder of the cheque to the
bank on which the cheque is drawn. Earlier it was six months from the date of the cheque.
Once the cheque becomes stale the payee or the holder has to approach the drawer for
revalidation of the cheque, which means the drawer puts the current date and authenticates
it by signing fully with or without the words revalidated. However due changes in the
process of clearing of cheques electronically where the original cheque is not presented to
the bank, but only a scanned image is being sent, the rules have been modified to accept
only cheques without any alterations. So the drawer has to issue a fresh cheque with the
current date in lieu of the stale cheque returned.
Mutilated Cheque: In case a cheque is torn into two or more pieces and presented for
payment, such a cheque is called a mutilated cheque. The bank will not make payment
against such a cheque without getting confirmation of the drawer. But if a cheque is torn at
the corners and no material fact is erased or cancelled, the bank may make payment against
such a cheque.
Dishonored Cheque: Normally when the cheque deposited by anybody for collection or
presented for payment at the teller counter, the banker makes payment of the cheque subject
to several conditions. When the cheque is returned by the banker for anyone or more
reasons by the banker, it is known as dishonour and the cheque thus dishonoured is known
as dishonoured cheque. Dishonour also known as bouncing or returning. It can be also
called as dishonoured cheque or bounced cheque or returned cheque. if the bank refuses to
pay the amount to the payee, the cheque is said to be dishonoured. In other words,
dishonour of cheque is a condition in which bank refuses to pay the amount of cheque to the
payee.
Whenever the cheque is dishonoured, the drawee bank instantly issues a „Cheque Return
Memo‟ to the payee banker specifying the reasons for dishonour. The payee banker
provides the memo and the dishonoured cheque to the payee. The payee has an option to
resubmit the cheque within three months of the date specified on the cheque after fulfilling
the reason for the dishonour of cheque.
Reason for dishonour of cheque.
If the cheque is overwritten.
If the signature is absent or the signature in the cheque does not match with the
25
specimen signature kept by the bank.
If the name of the payee is absent or not clearly written.
If the amount written in words and figures does not match with each other.
If the account number is not mentioned clearly or is altogether absent.
If the drawer orders the bank to stop payment on the cheque.
If the court of law has given an order to the bank to stop payment on the cheque.
If the drawer has closed the account before presenting the cheque.
If the fund in the bank account is insufficient to meet the payment of the cheque.
If the bank receives the information regarding the death or lunacy or insolvency of
the drawer.
If any alteration made on the cheque is not proved by the drawer by giving his/her
signature.
If the date is not mentioned or written incorrectly or the date mentioned is of three
months before.
4.7 CROSSING OF CHEQUE
Crossing of a cheque is nothing but instructing the banker to pay the specified sum through
the banker only, i.e. the amount on the cheque has to be deposited directly to the bank
account of the payee.Hence, it is not instantly encashed by the holder presenting the cheque
at the bank counter. If any cheque contains such an instruction, it is called a crossed cheque.
Purpose of Crossing
A crossing is an instruction to the paying banker to pay the amount of cheque to a particular
banker and not over the counter. The crossing of the cheque secures the payment to a
banker. It also traces the person so receiving the amount of cheque. Addition of words „Not
negotiable‟ or „Account Payee only‟ is necessary to restrain the negotiability of the cheque.
The crossing of a cheque ensures security and protection to the holder.

26
Types Of Cheque Crossing
General Crossing – cheque bears across its face an addition of two parallel
transverse lines.
Special Crossing – cheque bears across its face an addition of the banker‟s name.
Restrictive Crossing – It directs the collecting banker that he needs to credit the
amount of cheque only to the account of the payee.
Non-Negotiable Crossing – It is when the words „Not Negotiable‟ are written
between the two parallel transverse lines.
General Crossing:
Section 123 of The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 defines General Crossing as: “Where
a cheque bears across its face an addition of the words “and company” or any abbreviation
thereof, between two parallel transverse lines, or of two parallel transverse lines simply,
either with or without the words “not negotiable”, that addition shall be deemed a crossing,
and the cheque shall be deemed to be crossed generally”.
Two parallel transverse lines are drawn on the face of the cheque, generally, on the
top left corner of the cheque
Holder or payee cannot get the payment at the counter but through the bank only
Including the name of the banker is not essential, hence, the amount can be encashed
by any banker
The words, “& Company”, “Not Negotiable”, “A/C. Payee” may or may not be
written
It can be converted into Special Crossing

27
Special Crossing: When a cheque bears the name of the bank in between the two parallel
lines, with or without the words 'not negotiable' is called Special Crossing. The bank will
pay to the banker whose name is written in between the crossing lines.
Restrictive Cheque Crossing or Account Payee’s Crossing: This type of crossing
restricts the negotiability of the cheque. It directs the collecting banker that he needs to
credit the amount of cheque only to the account of the payee, or the party named or his
agent
Not Negotiable crossing: The effect of Not Negotiable crossing is that cheque lost its
essential feature of “a Negotiable Instrument”. The Transferee of such crossed cheque can
not get a better title than that of the transferor (cannot become holder in due course) amd
cannot convey a better title to his own transferee but the instrument remains transferable.
Questions
PART A
1. Enumerate the reasons for dishonour of a cheque .
2. List the various types of deposits accepted by banks.
3. Differentiate between cheques and demand draft.
4. State briefly the various forms used in banks.
5. Distinguish between fixed deposit Account and Savings Deposit Account
6. Classify various types of cheques.
7. Outline the significance of crossing of cheques.
8. Differentiate between NEFT and RTGS
9. Describe overdraft facility provided by commercial banks.
10. Differentiate between cheque and demand draft.
28
PART B
11. Describe the importance of banks for business
12. Critically evaluate the different modes of money transfer.
13. Discuss in detail various types of bank accounts.
14. Explain the significance of various bank documents.
15. Classify the retail payment system.
16. Explain Mobile banking. How does it differ from using a mobile phone for making
payments.
References
1. Banking Theory Law and Practice- S.N.Maheswari and S.K. Maheswari
2. Banking Theory Law and Practice- Dr.V. Radha
3.Banking Theory Law and Practice- Dr. S. Guruswamy
4. Banking Theory Law and Practice- B. Santhanam

1
SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT STUDIES
UNIT – V – OFFICE MANAGEMENT – SBAA1407

2
V. ROLE OF SECRETARY
5.1 PRIVATE SECRETARY
A Private Secretary or Personal Assistant is the backbone of an organisation, whose
work requires a variety of project management, communication and organizational skills.
The work profile of a Secretary of today is not the same as was in decades past. The job
responsibilities have evolved to acquire much more advanced skill set such as mastering
Microsoft Office applications, drafting correspondence, preparing presentations, managing
budgets, maintaining websites, preparing expense reports etc. Secretaries might also
manage all the administrative details of running a high-level conference or meeting and be
responsible for arranging the catering for a lunch meeting. Often executives will ask their
assistant to take the minutes at meetings and prepare meeting documents for review. In
addition, a Secretary may be responsible for keeping all of the official records of a
company or organization. Hence, Secretary is an assistant to an executive, possessing
mastery of office skills who is supposed to have an ability to assume responsibility without
direct supervision, the one who displays initiative, exercises judgement and makes
decision within the scope of his/her authority. In other words, a Secretary is an assistant
who performs routine and special duties on behalf of an Executive (Boss) in an office.
Definition
The word Secretary is derived from the Latin word ―Secretarius‖ which means ―a
confidential person‖. As the word conveys an idea of secrecy, the title of Secretary is
generally used to apply to an official who conducts confidential correspondence and
performs such works. However, in today‘s world, the duties of a Secretary have become so
varied that a modern secretary is no longer just restricted to performing confidential work.
A Secretary is, also sometimes called Personal Assistant, Executive Assistant or
Professional Secretary etc. and considered to work for CEO, Chairman, Managing
Director, Chief Manager, Departmental Heads and so on. Today, the profile of a Secretary
has completely changed. A Secretary has to be responsible person to whom an executive
can delegate his/her routine duties, entrust confidential matters with full confidence to act
on his/her behalf whenever necessary.
The secretary has been defined as ―A person who assists the management in
achieving the objectives of the organization. He is entrusted with secrets and confidential
matters of his master/ employer. He records all the relevant informations for future
reference and vital decision making purposes. The secretary is entrusted with work such as

3
administering the office, and related office work, conducting periodical meetings, co-
ordinating departmental work, to have cordial relationship with public in connection with
related official work, to develop company image in the society, to write suitable
correspondence to various offices/authorities etc.,‖
A Secretary is appointed to assist executives in all types of organization; whether
commercial, manufacturing, industrial, educational or any other type. However, the
functions and duties of a Secretary vary according to the nature and size of an
organization. Basically, every Secretary has to perform certain routine duties. In an
organization, generally, a Personal Assistant is a junior official who has to perform the
duties of a Front Office Assistant or a Stenographer, whereas a Private Secretary is usually
attached to a top executive who has to perform such duties which require higher level of
secretarial skills. He/She is considered as a link between the executive and the junior
officials to facilitate implementation of the decisions taken. Nowa-days, every Private
Secretary is supposed to be administrative specialist and well trained member of an office
team
5.1.2 Importance of a Secretary
A Secretary is considered to be the backbone of an organization and plays an important
indispensable part in the conduct of business in government, professional, commercial and
industrial organizations of all kinds. The Secretary attends to the time-consuming details
of the work of the executive and helps him/her to do the job in a better way. It is the
Secretary who takes care of office mail, prepares drafts, answers phone calls, do record
management, makes tour programmes, operates bank transactions, arranges meetings and
prepares minutes of meeting. It is well said that the success of an executive mainly
depends on the competence of his/her Secretary. There is always an able secretary behind
an able executive. A secretary not only does what he/she is told to do but also does
whatever is required for the proper discharge of the assigned tasks. The Secretary‘s job is
not limited to carrying out the instructions but his/her responsibility is also of advising the
executive on various administrative matters whenever required. At times, a Secretary
serves as the ears, eyes, memory and hands of the executive.
5.2 APPOINTMENT
An important and busy man cannot and should not waste his valuable and scarce time for
doing routine types of jobs. Persons of eminence such as industrialists, politicians,
directors of a com-pany, doctors, lawyers, important authors, film stars appoint private
4
secretaries to assist them in their personal and confidential matters. When a private
secretary is appointed by an individual, the terms and conditions of his appoint-ment are
determined by his master. When a private secretary is appointed by an organisation as its
Chief Executive, the terms and conditions of his appointment are determined by the rules
and regu-lations of the organisation concerned.
5.3 DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PRIVATE SECRETARY AND COMPANY
SECRETARY
A personal secretary is the one who does office work and administrative work. It is a job
title of describing a person who assists a specific person with their daily business tasks. A
company secretary is responsible for the administration of the company with regards to
compliance with statutory and regulatory requirements. A company secretary is a
representative who is responsible for running the company without any irregularities as per
the law. The key differences are any individual can become a secretary after going
through a secretarial course but those who have studied CS alone can become a company
secretary. The key differences between the two is their responsibility, emoluments, what
they need to do, report on office etc.
Personal Secretary
Company Secretary
An individual employed by a busy
person to look after his official,
professional, private and personal work
is called a personal secretary.
According to the Companies Act 1956, an
individual processing the prescribed
qualification and appointed to performed the
duties of a secretary under the act and any
other ministerial or administration duties, is
called a company secretary.
There is no prescribed qualification for
the appointment of Personal Secretary.
However, he is required to have the
knowledge of information technology,
book-keeping and office routine.
The secretary shall have the prescribed
qualification and should be a member from
the Institute of Company Secretaries of India
(ICSI).
5
A Personal Secretary is appointed by
busy individuals such as industrialists,
doctors, lawyers, actors, ministers,
political leaders, businessmen etc.
A Company Secretary is appointed by the
Board of Directors in the company. His
appointment is compulsory by law in case of
company having paid up capital of Rs. 5
Crore or more.
Personal Secretary has no legal status.
Company Secretary has legal status.
He is personal assistant of his boss or
employer.
He is the Chief Executive Officer of the
company and one of the Key Managerial
Personnel (KMP).
He is given limited powers by his boss or
employer.
He derives certain powers from the
Companies Act and certain powers from the
board of directors.
5.3 DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF A SECRETARY
In view of global era and development in IT skills, work profile of secretary has entirely
changed. Earlier, even the managers at junior level were also taking secretarial help in order
to discharge their duties. But since the advent of computers, usually the junior and, to some
extent, middle levelmanagers are performing most of their routine administrative jobs like
preparing letters, sending of mails, record management, etc. on their own. However, top
management level and senior executives do have to delegate their routine administrative
tasks to their Private Secretary. With this change in scenario, it is evident that the secretarial
work requires lots of expertise and skills as usually every Private Secretary has to directly
report to senior executives in an organization.
It is generally noted that no two private secretaries perform exactly the same work.
Therefore, one cannot lay down an arbitrary list of duties. A PS to a junior executive has to
work as a Front Office Assistant, Stenographer, Multi-Tasking Assistant etc. while a PS to
the senior executive has to collect information on different topics, draft reports and speeches,
write down the proceedings of the meetings/seminars and give advice to the executive on
certain administrative matters. That is why a definite list of duties of a PA/PS cannot be laid
down.
Usually, the duty performed by a Private Secretary depends on the:
6
Skills, personality and intelligence of a Secretary
Size of an organization where the secretary is working
Position of the executive with whom the secretary is working
Willingness of the executive to delegate authority and
Secretary‘s willingness to assume responsibility
1. Routine Office Work:
Every private secre-tary has to perform some routine official work which depends on the
nature of the status of his employer. Routine office work of a private secretary in-clude
handling of correspondence, maintaining records including filing and indexing, maintaining
various records, books of accounts and registers etc., attending telephone calls and callers,
preparing tour programmes of his employer etc.
2. Literary Duties:
Every private secretary must be a good stenographer capable of taking dictations from his
employer and typing them out. He has to draft routine correspondence for his employer. He
has to draft speeches, reports or statements as may be asked by his employer.
3. Receptionist‘s Duties:
Every private sec-retary has to act as a receptionist. He has to handle telephone calls—both
incoming and outgoing. He attends the callers and answers their questions on behalf of his
master. He maintains a diary for the engagements of his employer.
4. Duties Relating to Meetings:
The private secretary of a prominent person connected with so-cial or political organisations
is frequently asked to act as a secretary to various committees and sub-committees. He has to
prepare and issue notices for meetings, he has to conduct the meeting and prepare the
minutes of the meetings. Sometimes, the private secretary prepares the speech to be delivered
by his employer at the meet-ing.
5. Household and Social Duties:
Sometimes the private secretary holds a residential post. In that case, he has to perform many
duties in connection with his employer‘s household and social affairs, as:
To arrange for the payment of wages and salaries of domestic staff;
To maintain personal accounts of his em-ployer and submit his income tax re-turns;
7
To maintain investment records of his employer;
To pay for electric, telephone and other bills;
To arrange for purchase of tickets, hotel reservation, railway reservation etc.;
To make arrangements for parties, din-ners, get-together and other engage-ments, to
send greeting cards, letters of congratulations etc.
6. Financial Duties Of Office Secretary:
The main financial duties of a private secretary will be:
Handling the cash and bank accounts of his employer;
Payment of bills, taxes, salaries, sub-scriptions and donations and keeping their
records;
Keeping records of the employer‘s investments and the income derived there-from;
Preparing the income tax returns and fil-ing them before time and payment of
in-come tax to the government;
Making payments for insurance policies.
7. Miscellaneous Duties
Private Secretary has to perform some miscellaneous duties, like to:
Prepare Power Point Presentations on various topics.
Work as Data Entry Operator.
Present concise information when the officer has to sit for an interview.
Draft reports and speeches for meetings and workshops, etc.
Supervise junior employees and their training, etc.
Act as a liaison officer between the employer and the employees.
Advise executive on purchase of office machine/equipment and stationery, etc.
In order to perform secretarial duties the most efficiently and effectively, it is necessary for a
Private Secretary to be competent in IT and secretarial skills. Today, an efficient Private
secretary is a combination of secretarial plus managerial skills, as he/she has to often report
directly to senior executives and take care of multiple administrative responsibilities.
8
5.4 QUALIFICATIONS AND PERSONAL QUALITIES OF A SECRETARY
To perform the secretarial duties with confidence and efficiency, a Private Secretary requires
many qualities and skills as well as a wide general education. These qualifications and
qualities are discussed below.
a) Academic Qualification
The education develops mind of a person and enables a person to appreciate better the total
environment. A senior level Secretary is usually a graduate. It is generally said that, the more
the education, the greater is the awareness and better power of understanding, grasping and
expression.
b) Vocational Course of Secretarial Practice or Office Management
A course in Secretarial Practice is a very useful attribute for a Private Secretary.
Opportunities for high level secretarial jobs and promotion come often to those who have
broad general education with a vocational course in Secretarial Practice or Office
Management. The course includes mastery of various subjects viz. Stenography, Computer
Operation, Office Procedure, Business Communication, etc.
c) Mastery of IT and Secretarial Skills
A Private Secretary must have a complete mastery of some basic skills which are the
essential tools of his/her trade. Complete knowledge of word processing, preparation of
spread sheets, using internet, locating information from various sources, sending e mails etc.
is must. Besides, he/she must be able to take dictation rapidly and transcribe the same
accurately. He/she must be fast and accurate on the computer. The letters and other material
typed by them should always be neat and well arranged along with flair to present error-free
work for signature, except in those cases where only a rough draft is called for. Other
secretarial skills include mastery on record management, reprography, ability to write
correctly and to the point, to answer telephone calls, to deal with visitors, to meet people and
talk with them pleasantly.
To be able to assist top executives, locating information on a variety of topics for him/her
and dealing with a variety of people coming into the office, one should have knowledge of
the recent developments in political, economic and social fields and have an awareness of
national and international events. It can be achieved by regular reading newspapers,
periodicals, journals and magazines etc.
9
d) Good Communication Skills
A large part of Secretary‘s work consists of correspondence and preparation of notices,
agenda, minutes, reports, speeches etc. Therefore, to be a successful Secretary, one should
have a good command over the oral and written communication skills. Business in majority
of offices in India is carried on in English language. In this global era, English also serve as a
language of commercial contact between different countries. Therefore, a Secretary should
have sound knowledge of English. Skill in shorthand is of no use without proficiency in
language. A Secretary should preferably have the knowledge of the regional language too. If
the organization has dealings with foreign institutions, it will be an advantage to have a
working knowledge of one or more foreign languages also.
e) Knowledge of the Profession or Business of the Employer
Besides the above, one should be thoroughly familiar with the objectives and management of
the firm or organization for which one is working. In other words, one should know the full
range of activities of the organization, strong personalities, key figures in any particular field
of activity along with duties and responsibilities of the executive with whom one is working.
The more one knows about the organization, the better job one will be able to do.
f) Personal Qualities of a Secretary
A Secretary should possess a variety of soft skills to be successful and develop calm, positive
personality. Some of the important personal qualities relevant for the job a Private Secretary
are discussed below:
• Adaptability
If Private Secretary has got the quality of adaptability, adjustment under all the situations in
office becomes easy and less straining. It is important that a Private Secretary should be
adaptable to all kinds of people, situations and problems. Sometimes, it may happen that one
executive is transferred and the new executive takes over. The new executive might not be
having the same nature or temperament. Also, there may be heavy work at one time due to
certain deadlines but may not be much work in office at any other time. Thus, a Secretary
should inculcate habit of adjusting with different types of persons/situations.
• Cooperative Attitude
In an organization, cooperativeness means assisting every member with a courteous and
helpful attitude including exercising self-control at times of extra pressure. It is teamwork
10
that counts in an organization. A Secretary should cooperate with every member of the
organization, from the highest to the lowest in rank. Cooperativeness enhances respect of a
Secretary. The urgency of work may require, sometimes, to sit late in the office or to attend
office during holidays. If the exigencies of work require it, one should try to understand the
situation with a cooperative attitude.
• Courtesy
A Secretary should show proper consideration for all members of the organization as well as
to outside callers. Courtesy may be shown in greeting each member and visitor pleasantly,
offering a seat, etc. and with use of words such as ‗Please‘ or ‗Thank you‘, whenever
required.
• Loyalty
To be loyal means faithful to the employer and always helpful to him/her. A Secretary should
be dedicated to the job and do assigned work honestly and sincerely. Loyalty is critical
quality for holding a secretarial position. In order to be loyal to your executive and to the
company or firm or institution for which you work, you must be familiar with the executive‘s
goals and the organization‘s overall objectives and work at all times towards the goals.
• Punctuality
Punctuality means available to the executive for work at the desired time and also to finish
the assigned job at the proper time. This simple but significant quality is very essential for a
Secretary. One must not be a ‗Late Starter‘ or ‗Early Stopper‘. It is very annoying for an
executive to find his/her Secretary absent when something requiring immediate attention
comes up suddenly.
• Tactfulness
Tact enables one to act in a particular fashion under particular situation. It is the personal
skill of saying or doing what is required by the circumstances, the ability to handle a difficult
situation in a right and positive manner. It has been truly called the ―fine art of avoiding
offence‖. A Secretary is called upon to exercise tact in dealing with his/her employer,
colleagues, visitors, etc. Judgement and discrimination are essential to become tactful.
11
• Pleasing Voice
A Secretary should have a low but confident well-controlled and pleasing voice. A pleasant,
clear voice is attractive while loud and demanding voice is unattractive. It has also to be
understood that a very low and retiring voice makes communication difficult.
• Personality and Poise
Personality is usually linked to what you are, what you do and how you do it. Personality
makes one person different from another. It is not important what kind of physical features
you have, but rather the expression on those features. Good personality creates a positive
impact on other people. Poise is getting along with people well without superior or inferior
feeling. It comes from knowing one‘s abilities as well as limitations. Poise enables a
secretary to be at ease and also to make others feel at ease. It is rightly said that knowing that
you are well-groomed will give you confidence and confidence gives you poise.
• Good Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal skills are the skills which help a person to interact with others properly. In an
organizational setting, it is the ability to get along well with other members; whether senior
or junior. It is important for a Secretary to possess excellent interpersonal skills to facilitate
effective working relationships.
5.5 MODERN TECHNOLOGY AND OFFICE COMMUNICATION
Modern Technology –Internet, multimedia,Scanner
Modern forms of Communication – fax, email, voice mail, video-conferencing
and web-casting
Changing technologies including personal computers (PCs), projectors, multimedia
systems, and the Internet—have had a major impact on the office environment. The ability
to use technology is an essential skill in the ever changing workforce. Offices in today's
society are transmitting information via electronic mail (e-mail), electronic calendars, and
teleconferencing, as well as other electronic devices. Communication via technology is just
as important as oral and written communication in the work environment. Technology
continues to play a vital role in transforming the business environment.
5.5.1 Personal Computer
The invention of the PC in the 1980s altered the way computing power was distributed
12
within an organization—changing how companies were run, the ways in which
information was created, and the ways in which information was used by individuals in
carrying out their jobs. The use of word processing and spreadsheet packages made it
possible for professional staffs to create their own reports without having to go to a central
typing pool or computer center. Prior to the advent of the PC, secretaries typed letters,
created reports, and organized information in files. The nature of secretarial positions
changed with the arrival of the PC, from a focus on document creation and production to a
focus on other kinds of administrative functions, as reflected in the changing work patterns
of the office.
Portable PCs
Portable PCs include personal digital assistants (PDAs), laptop computers, and notebook
computers. PDAs are proliferating. Among the most popular PDAs are the Palm and
BlackBerry. Laptop computers are used by business travelers to make multimedia
presentations, create and send reports and spreadsheets, and do research on the Internet.
Notebook computers are similar to laptops, but usually smaller.
Intranets and Internets
Messages can be transmitted electronically within an office (intranet) as well as around the
universe (Internet, or Net). Workers are able to exchange information over the computer
via the Net through e-mail. E-mails can be sent simultaneously to many individuals around
the world. The intranet is an internal computer network that is used within a company,
whereby pertinent information—such as telephone directories, calendars of events,
procedure manuals, job postings, and human resources information—can be posted and
updated. With the intranet, one is able to communicate online with individuals within a
designated work environment. The Internet is a global computer network that permits
millions of computers around the world to communicate via telephone systems and other
communication lines. It is also known as the digital information super-highway and is a
part of the World Wide Web. With the Internet one can communicate to anyone online
throughout the world. The Internet is a public worldwide computer network full of
information comprising inter-connected networks that span the globe.
13
5.5.2 MULTIMEDIA
Multimedia enhanced simple, text-only computer interface and production acquisition and
holding of attention and interest in measurable benefits. In short, is to improve multimedia
information retention. When it‘s properly constructed, can be profound and useful
multimedia entertainment. Multimedia can be use in many way are business, school, home,
public places and virtual reality.
Multimedia Usage in Business
Business applications in multimedia are presentation, training, marketing, advertising,
product demos, catalogues, networked communication and voicemail. The presentation is
very useful in many aspects of work and life. Because these are important in business to
sales, training, teaching, lecturing and generally entertaining an audience.
• Presentation allows us to lecture in front of audiences and to present our product or
project. Presentation can be use in oral, multimedia, power point presentations,
educational or training sessions to giving simply a talk on a subject to group a
voluntary basis for pleasure. In this is to facilitate small business and your employees,
customers and potential customers of communication.
• Multimedia in business marketing is easy to persuade the customers to buy us
products. In business have different customers they have teenage, elderly people and
many. So we can use the multimedia because that can make them easy to
understanding it. These are the most common photo sharing marketing strategies.
Multimedia is an effective and cheapest way to grab an attention of the visitors and
share information about various products easily. Advertising industry uses
multimedia for marketing various products.Today multimedia is very important to
promote any time of business easily and effectively.
• Website Design: Multimedia use over the past decade has been within website
development. Website design seamlessly meshing content, images, logos, audio and
video files with site navigation, is also big business, especially since businesses want
the best-looking sites that reflect their essential core and character.
5.5.3 SCANNER
A scanner is a computer hardware that uses reflected light to capture images and translate
them into files a computer can read and display. Scanners come in high- and low-
resolution versions, and can scan images in either black-and-white or color. The basic
14
functions of a scanner can be adapted to a wide variety of uses, depending on your needs.
These can include converting paper documents to digital formats and scanning receipts
into spreadsheets for your accounting department.
Backup and Storage
By scanning your paper files into a digital format and saving them in multiple
locations, including as an offsite server, you can eliminate the wasted space of paper
files while backing up important documents.
Transmitting to Colleagues and Customers
Getting information into the hands of your employees, customers and other business
contacts quickly can mean the difference between landing your next big account or
losing it to your competition.
Integrate With Your Office Software
Products such as Microsoft Office have built-in functions that allow you to scan
information directly into document and spreadsheet files. By activating the Optical
Character Recognition tools, characters on paper documents, receipts, order forms and
work orders may be transferred to the program of your choice to eliminate the need for
separate data entry.
Digitization and Preservation of Print Photos
One of the most common uses for a scanner is its ability to scan and save print photos
into digital formats such as JPEG or GIF. While digital cameras are widely available
and a common feature on devices such as smart phones, tablets and portable video
game devices, a scanner can convert printed photos to a digital file for use on your
company's website or to create a backup file.
5.6 MODERN FORMS OF COMMUNICATION
5.6.1 FAX
Just as the conventional telephone carries voice, a fax or facsimile machine carries printed
messages (words and pictures in photocopy form) from the sender instrument to the
receiver instrument. The sender of a fax message prepares the copy on a sheet (generally
no larger than A4 size) which can be fed into the fax machine. He dials the destination
number, gets the fax tone and feeds the message into the machine. The printed message is
converted into electronic signals as the paper rolls through the fax machine. This message
is received in the same form at the other end on the paper roll that is attached to the
machine.
15
Advantages of fax
1.
Universal Method of Communication: The fax machine has made it possible to send
copies of important documents including certificates, testimonials, degrees, agreements,
contracts etc. from one place to another at the speed of a telephone call. For this reason, it
is universally used method of communication.
2.
Sending Message Directly by Computer: If a document is generated on computer, it can
be sent directly using a fax modem, bypassing the need to print the document first.
3.
Advantage over Telex: Charts, graphs and other visuals cannot be sent through telex but
they can be easily sent thorough fax.
4.
Quickest Means of Communication: Fax is one of the quickest means of transmitting
information. In fax, the finally prepared document is inserted in the machine and almost
instantly copy of the document comes out at the receiving end.
Disadvantage of fax
a. It is expensive compared to email and post.
b. Sometimes the reception is blurred due to channel defects or mechanical failure at
either end.
c. At the receiving end, the message is printed at the receiver‘s cost. In case unwanted
messages pour in, the receiver has to bear the cost.
5.6.2 E-MAIL
Internet is an international computer network that links computers from sectors such as
government agencies, business houses, educational institutions and individuals. It receives
information, stores it and allows it to be read on satisfying certain conditions. Internet
Service Providers (ISPs) allow one to create the e-mail ID free, hoping to recover the cost
through the ads to which the user is exposed during the use of email. A typical email
address reads [email protected]. Some other ISPs are bsnl, yahoo, hotmail, and Gmail.
Note the use of only lower case (small) alphabets email in IDs.
Advantages of e-mails
1. Emails are easy to use. You can organize your daily correspondence, send and
receive electronic messages and save them on computers.
2. Emails are fast. They are delivered at once around the world. No other form of
written communication is as fast as an email.
3. The language used in emails is simple and informal
16
4. When you reply to an email you can attach the original message so that when you
answer the recipient knows what you are talking about. This is important if you get
hundreds of emails a day.
5. It is possible to send automated emails with a certain text. In such a way it is
possible to tell the sender that you are on vacation. These emails are called auto
responders
6. Emails do not use paper. They are environment friendly and save a lot of trees from
being cut down.
7. Emails can also have pictures in them. You can send birthday cards or newsletters
as emails.
Disadvantages of e-mails
1. Emails may carry viruses. These are small programs that harm your computer
system. They can read out your email address book and send themselves to a
number of people around the world.
2. Many people send unwanted emails to others. These are called spam mails. It
takes a lot of time to filter out the unwanted emails from those that are really
important.
3. Emails cannot really be used for official business documents. They may be lost
and you cannot sign them.
4. Your mailbox may get flooded with emails after a certain time so you have to
empty it from time to time.
5.6.3 VIDEO CONFERENCING
Videoconferencing, however, is the closest it gets to seeing and hearing one another
without being present together. The technologies used in a videoconference are: monitor
screen, camera, microphone, codec (compressor-decompress or), equipment control pad at
each location, and internet connectivity. With the passage of time, this is becoming more
popular and easier to use. You often see it in TV interviews. You often see it in TV
interviews. For a videoconference, the participants get into a special room at their
respective locations, equipped with the gadgetry. They can see, hear, speak to others and
show exhibits without physical presence together.
17
Advantages of video conferencing
1. No time constraint: Video conferencing can be conducted at any time of the day. Time
differences between countries do not matter when people use this method of
communication because they do not actually need to travel to attend meetings.
2. Dramatic travel saving: Not only is video conferencing a direct replacement for many
in- person business trip, but also there is virtually no cost for people to be involved in a
virtual meeting, you can easily bring the right them together.
3. Easy communication: People can use video conferencing to communicate with anyone
with HD video and other collaboration tools such as whiteboard, text exchange, file
sharing, media sharing, screen sharing, remote control, electronic voting, conference
recording etc.
4. Increased productivity: By eliminating time and district barriers, meetings can be hold
anytime, anywhere with anyone. In this way, meetings are shorter and more effective. And
also with the rich collaboration tools, decisions can be made faster.
Disadvantages of video conferencing
1. Lack of personal interaction: Some meetings require a personal touch to be successful.
Video conferencing can be less personal than meeting face to face, and it can be possible
to miss out on vital body language when you‘re struggling with a pixelated image or
stuttering video.
2. Technical problems: The major disadvantages are the technical difficulties associated
with smooth transmissions that could result from software, hardware or network failure.
Remote connections are sometimes known to be hampered by environmental changes. On
some occasions, the absence of technical support personnel creates difficulty for
participants who are unfamiliar with the videoconferencing technological concepts.
3. International time zones: One of the very real disadvantages of using video
conferencing is that if you communicate regularly with people in other countries you will
be available at different times to them. Unfortunately without the skills of a time lord
there‘s not really a practical way to overcome this.
4. High cost of setup: Setting up video conferencing in an office can be a bit expensive for
small-sized companies. Simple features can fit into the budget, but if advanced features are
required, then a substantial amount of expenditure must be done
18
5.6.4 VOICE MAIL
Electronic system for recording oral messages sent by telephone. Typically, the caller
hears a prerecorded message and then has an opportunity to leave a message in return. The
person called can then retrieve the message at a later time by entering specific codes on his
or her telephone. Voice mail is distinguished from an answering machine by its ability to
provide service to multiple phone lines and by the more sophisticated functions that it
offers in addition to recording message.
Advantages
1.
The messages may be created in the user‘s voice mailbox and then they are transported
to another voice mailbox , Voice messaging is a viable alternative to e- mail and fax
systems as a business communicating tool , The voice-messaging system improves the
public relations in the companies .
2.
The voice-messaging systems include many services such as the voice messages , the
voice-mail distribution lists , fax-in and fax-on demand in the mailbox , the interactive
voice response , and the voice forms that any user can access anywhere in the world .
3.
Voice mail provides twenty-four-hour-a-day answering capability , It can enhance the
efficiency and boost the job productivity , It can save and generate the money for the
company , It can improve the accuracy of message content and it can enable one to send
multiple messages to the people .
4.
Voice mail can allow the messages to be easily updated , It can reduce the need for
administrative / receptionist / secretarial support , It can serve as an important medium
for business communication , It can make transferring of phone calls from department to
department easier and more efficient .
5.
You no longer miss any calls when the people leave the messages on your voice mail,
You can listen to your messages , You will remember your schedules and it will keep
you in the loop .
6.
Your callers will be able to get in touch with you by leaving you a voice mail message,
Instead of calling you until they get hold of you , they can leave the message, their
name, and the phone number .
7.
A well-implemented voice mail system can provide the benefits to the customer and the
business , The customers can leave a message at any time , without waiting on hold or
navigating the system .
19
Disadvantages
1.
Some people cannot use the voice-messaging systems, The voice-messaging
system is less economical for the smaller companies, Some people do not see any
benefit in having a voice mailing system in place, It will be a nuisance for them.
2.
Some people do not like that they cannot reach a live person, when there are too
many voice-messaging options that may make it difficult for people to recall which
options they used previously.
3.
If you miss a lot of calls that you will be flooded by many voicemail messages ,
Listening to the voice mail is very tiring and time consuming , you can use your
time doing more important and urgent tasks .
4.
You will get tired of listening to the messages and end up deleting the messages
without listening to them, this cause you to miss the important messages.
5.
The message recording systems can fall prey to the hackers who phish the
passwords through spam email or social engineering, They can access to the
messages , They can take the personally identifiable or proprietary business
information .
5.6.5 WEB CASTING
Webcasting is the process of video broadcasting live over the internet. This technology
operates in real-time and allows for active conversations among and between the webcaster
and their viewers. Recent developments in technology have made this both an affordable
and an effective tool for communication. Embracing webcasting as a marketing initiative
for your company is beneficial in that it is a popular, new trend, allows for direct
communication with your audience, and can portray to your customers that you are a
subject matter expert.
Advantages
1. Cost. Whether you are trying to advertise a product, service or simply trying to share a
certain message, webcasting is definitely a more cost effective way to do this. Traditional
broadcasting requires the use of satellites that is more expensive to connect to than the
streaming platform on the internet. These days several apps on smartphones and other
mobile devices give the user the option to live stream on social media and other platforms
at simply the cost of your internet service subscription. Webcasting is an cost efficient way
of advertisement.
20
2. Audience. Because it uses the internet as its platform, webcasting allows the presenter
to access a large number of viewers at the same time. Millions of people use the internet in
one second and webcasting exposes you to all these internet users. Effectively using the
already existing internet traffic is another advantage of webcasting as a communication
tool.
3. Mobile Devices. If you like what you watched on the webcast, you can always save the
video on your mobile device and save it for later. Sites such as ezTalks has a catalogue of
easy to access webcasts that you can always go back and visit even if you did not catch
the live stream. It is less convenient to save and access satellite broadcasts after their first
showing or release.
4. Target Audience. Webcasting has an advantage over print when it comes to the
advertising sector. This is because, when you buy a catalogue or a magazine the editor has
no way of knowing what captivates your interest. The best they can do is place in their
magazine content that seems to be popular within your demographic. This is where the
advantage of webcasting comes in. When a consumer is searching for a particular product
online can be targeted by a webcast whose concept is based on that specific product.
Disadvantages
1.
Internet Connectivity Disruptions. Webcasting relies solely on the effectiveness of
internet connectivity and reliability. If you are in an area that experiences poor internet
connection or disruptions in the network, then this mode of communication will not be
appropriate or effective because the quality of the cast will be severely compromised.
Some of the disruptions that you may experience due to poor connectivity include loss in
audio, video distortion and lags in the transmission. The disadvantage of webcasting here
is that the internet stands a higher chance of disruptions than satellite broadcasting.
2.
Non-Interactions. This mode of broadcasting is not one that allows for two-way
interactions. There is limited engagement between the presenter and the viewer. This
means that webcasting is not an appropriate method of interactivity oriented
communication. You, as the viewer, do not have the opportunity to ask questions or seek
clarification on the same forum. If you need clarification you will have to attend another
forum to get this, making it less convenient than a forum that is interactive in real time.
3.
Professional, Audio and Visual Specialist. For higher quality webcasts, you will need
to hire professional audio and visual communication specialist who are familiar with the
appropriate settings and strategic bandwidth specifications. You will need special cameras,
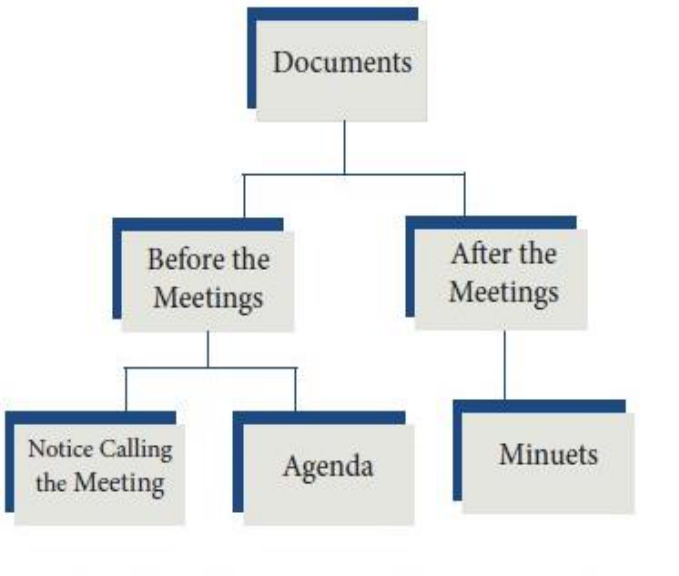
21
lighting and audio devices which will obviously incur your costs. This extra cost in your
budget is a definite disadvantage. For business needs, you may need to seek out
professional companies that specialize in video conferencing and offer the required
equipment.
5.7 MEETING
A meeting is an interaction between people, held for the purpose of achieving a common
goal through verbal communication, such as sharing information or reaching agreement
about a new idea, a new opportunity, a problem, or to brainstorm something with an aim to
take right decision.It may occur face-to-face or virtually, as facilitated by communication
technology such as a telephone, conference calls, a Skype conference call or a
videoconference. Business organizations often hold meetings with an intention to increase
efficiency and productivity.
5.7.1 DOCUMENTS TO BE PREPARED BEFORE AND AFTER MEETINGS:
The most essential documents needed to be prepared in connection with meeting are Notice,
Agenda and Minutes. Of these, Notice and Agenda are prepared before the meeting and
Minutes is prepared after the completion of meeting.
22
Notice Calling the Meeting:
When a meeting is to be conducted, a notice is required to be sent to all the members.
A Notice is an intimation about the conduction of the meeting. Generally, it is typed or
printed on the organizations‘ letterhead and issued under proper authority. Notice of the
meeting must include the following content
The name of the organisation.
Day, date, and time.
Place of the meeting. i.e. the address and the specific room/hall
Purpose of the meeting and, if possible, the Agenda.
Date of circulation and conveners‘ secretary‘s signature
Agendas are the documents that give those attending meetings prior notice of what is being
discussed. Agendas also give all the relevant details of when and where the meetings take
place and who attends. Normally they have reports attached. Agenda means things to be
done. Agenda is document that outlines the contents of a forth coming meet. It is programme
schedule of the meeting and prepared by convenor or secretary in consultation with
chairperson and his approval and sent along with the notice of the meeting in order to enable
the members to come prepare for discussion during the meeting. An agenda should cover the
following.
Importance or necessities of Agenda:
a. As it is circulated in advance, it helps the member to come prepared for the
meeting.
b. Since agenda has a set order, it help the chairperson to conduct the meeting
smoothly.
c. It ensures that only matters relevant to that particular meeting are discussed.
d. It makes sure that every point is properly taken up for discussion.
e. Agenda facilitates the preparation of the minutes
Minutes are the formal record of what was decided at the meeting. They also tell you who
was present. Minutes is a record of the decisions taken at a formal meeting. All companies,
statutory bodies, social organisations, associations and committees have to maintain a record
23
of the meetings. As minutes are the official record of work done and decision taken at the
meeting, it must be precise and clear. Once minutes are approved and signed, it can be even
accepted by the court of law as evidence of the proceedings of meeting. The main objective
of minutes is to record, concisely and accurately, the essential work done at a meeting. The
minutes of companies and statutory bodies are written in formal style. Before you start taking
notes, it‘s important to understand the type of information you need to record at the meeting.
As noted earlier, your organization may have required content and a specific format that
you‘ll need to follow, but generally, meeting minutes usually include the following:
1. The name of the organisation.
2. Day, date, time and place
3. Number in order (e.g. 33rd meeting of …….)
4. Names of chairperson and secretary
5. Names of members present
6. Names of the members absent.
7. Attendees by special invitation, e.g. auditor, caterer, banker, etc.,
8. Record of the transactions.
9. Signature of the secretary after approval of minutes by the chairman.
5.8 DRAFTING, FAX-MESSAGES, EMAIL
An effective correspondence ensures efficient and economical communication service. The
drafting of correspondence improves the goodwill of the organization. The responsibility
of drafting a correspondence is based on the nature of correspondence and type of an
organization. Generally, routine correspondence is drafted by lower level Clerks.
Important and confidential correspondences are drafted by the top executives of an
organization. In large organization, the volume of correspondence is also large. Therefore,
a separate department or section is created for production and dealing of Correspondence.
5.8.1 Stages In Drafting
The following stages are involved while production or drafting of correspondence and
despatch the same to the parties.
1.
The required message or information is collected from various sources.
2.
The style of letter is decided according to the nature of correspondence.
3.
A rough copy is prepared at initial stage.
24
4.
The rough copy is forwarded to proper official for necessary adding, deleting or
correction.
5.
Once again the rough copy is read by the employee who has prepared rough copy.
6.
The rough copy is hand over to the typist or computer programmer for production
as the case may be.
7.
Again the produced copy is read by a person who has drafted the copy. The
correction may be made if any.
8.
The produced copy is arranged for getting sign from the concerned responsible
official.
9.
The signed copy is also verified by the employee who is dealing the
correspondence.
10.
Now, the letter is ready for dispatch.
5.8.2 Principles Of Drafting Of Correspondence
Little Field and Rachel have laid down the principles of drafting of correspondence.
a. Determine Purpose: Generally, there is a primary purpose of conveying some
information and the secondary purpose of conveying a feeling of helpfulness and
goodwill.
b. Planning of Message: Ideas have to be collected from across the o8ice and arrange
them in a logical order before the communication begins.
c. Using of Language: Conversational language has to be selected for the purpose of
clear cut directions and simplicity.
d. Be Compact and Clean: The message should results in the completion of job.
Every question should be answered in the communication.
e. Brief: There must be a thorough explanation of every point in brief.
f. Courtesy: Every communication should be courtesy, considerate, friendly and
helpful.
g. Read Proof Carefully: An excellent document can be ruined by grammatical and
typing errors. The typing error may be relating to spelling name, improper
arrangement of words and letters, wrong numbers and in sequence of sentences.
Besides, there is a possibility of failing to enclose necessary items. Hence, careful
proof reading is necessary for complete valuable correspondence.
25
5.9 MAINTENANCE OF APPOINTMENT DIARY
The basic principles of maintenance of appointment diary are as follows
1. Single point of control. There must be ONE PLACE, electronic or on paper, where
ALL the appointments are noted. Nothing must EVER be written down elsewhere, or
chaos will ensue. You may have a system where the constituency offices have a separate
system to the Westminster one, Calendar can be accessed from any computer, or from the
Member‘s phone or tablet, there really is no excuse for anyone not to know what is in the
diary nor there need any to duplicate the diary anywhere else.
2
Knowledge is everything. The best diaries will have all the information needed to hand
in advance, somewhere easily accessible.
3
MD engagement. The contents of the diary must somehow be transferred to the MD.
He or she must know where they have to be, when, and why.
If your MD manages their own diary, wrest it from their hands. No MDs should be running
their own diary as they should be getting on and doing the job of being an MD. Yet, some
MDs still try to organise their own time for fear of the consequences if the diary is
mismanaged. Allowing them to manage the diary also means that you will end up with
appointments entitled simply ―meeting‖ or ―tea‖ entered into the diary, whose details you
will be expected to mind-read 5 minutes before they are due to take place.
5.9.1 Diary Management
1. Selecting diary appointments. On the average day, you may receive dozens of
invitations for your MD and, even if they wanted to, they can‘t go to them all. It is up to
them what they do go to, but the basic principle is that there should be a real reason for
each appointment. Otherwise, they will never get anything else done.
2. Responding to diary appointments. This is also a good opportunity to clarify exactly
what the nature of the event is and what will be expected of your MD – is it a round-table
discussion which they will need to prepare for? Will there be a photo opportunity to which
the MD may want to take their own camera? Will they be asked to speak? In line with the
principle of ‗Knowledge is Everything‘, find out exactly what the nature of the event is
now to save time later
3. Declining invitations. Clearly, for constituency invitations, you will almost always want
to contact the organisation to give apologies if the MD can‘t attend, and the situation is the
same for particularly relevant organisations e.g. that your MD has worked with in the past
26
or otherwise has links with. However, realistically, you may decide that it is not the best
use of staff time to respond to hundreds of invitations a week, especially those which have
been sent (spammed) to every single MD and clearly have no bearing on your MD‘s work.
Some offices do respond to everything and that‘s great, but it‘s also OK not to.
4. Declining an open-ended invitation. It is often very difficult to decline an invitation
that has no date – ―Please can you meet with us at your convenience‖. You can always cite
a very busy schedule in the coming months but under those circumstances, they are likely
to repeat the request periodically. Wherever possible, try to be frank about the reasons for
declining and encourage the organiser to make a representation in writing instead. Useful
lines I have used are…
―It‘s not going to be possible to have a meeting because last time he met you, your press
release to the local papers completely misrepresented his views. Under these
circumstances, it might be better to write to him about your concerns‖. Sometimes you
just have to tell people something they don‘t want to hear.
5. Recording appointments: Many Researchers will agree that the fail-safe approach is to
enter everything in the diary from Select Committee meetings to haircuts. This ensures
double booking is less likely, especially if you share control of the diary with staff in the
constituency.
5.9.2 Electronic Diaries
Electronic Diaries are a way of keeping a copy of a diary on a computer. This allows the user
to browse their appointments, and mark appointments on electronic "diary pages". Since the
computer holds the details of each appointment users can be reminded in advance of
meetings and appointments. The use of computers also introduces flexibility into the format
of diaries, presenting different views, such as by year, month or week. Unlike a paper diary,
the computer automatically adds new pages when needed, extra room for each day, and
retains copies of diaries for years gone past.
While this is useful, the most important advantage of an electronic diary over a paper one is
in its ability to be shared. Unlike a paper diary, which is bound to one place, staff can access
an electronic diary over a computer network, checking to see when other staff are free.
Moreover, staff can share a diary, allowing a secretary to run a manager's diary, while still
allowing the manager access over the computer network. Electronic diaries held on desktop
computers, then, make booking meetings much easier. An electronic diaries allows meetings
times to be found, arranged, and confirmed, all from the computer, saving time and bother.
27
Questions
PART A
1. Describe the importance of secretary in business world.
2. Explain the qualification possessed by a secretary.
3. Differentiate between private secretary and company secretary.
4. State the contents of minutes of meeting.
5. Evaluate video conferencing as a form of office communication.
6. Outline the significance of multimedia usage in business.
7. Describe the implication of scanners in office.
8. Describe documents prepared in connection with office meeting.
9. State the principles of maintain office diary.
10. Bringout the importance of agenda.
PART B
11. Discuss the role of a secretary in modern office.
12. Discuss the duties and responsibilities of a secretary.
13. Explain the significance of modern technology in office communication
14. Classify the modern forms of communication in office.
15. Elaborate web casting and its merits to the organization
16. Describe the stages in drafting a correspondence.
References
1. Office Management By J.C.Denyer
2. Modern Office Management By Little Field CL and Peterson RL
3. Office Management- By P.K. Ghosh
